Table of Contents
- What is Order Fulfillment and Why is it Important?
- What are Order Fulfillment Centers?
- What are the Different Order Fulfillment Methods?
- How to Determine Your Order Fulfillment Strategy?
- Steps in an Order Fulfillment Process
- What are the Best Practices to Improve Your Order Fulfillment Process?
- How to Address the Key Order Fulfillment Challenges?
- Conclusion
What is Order Fulfillment and Why is it Important?
Order fulfillment is the complete process through which a business ensures that a customer’s order moves from storage to successful delivery. It involves multiple coordinated steps, starting with order picking, packing, and dispatching to the end consumer through trusted shipping carriers.
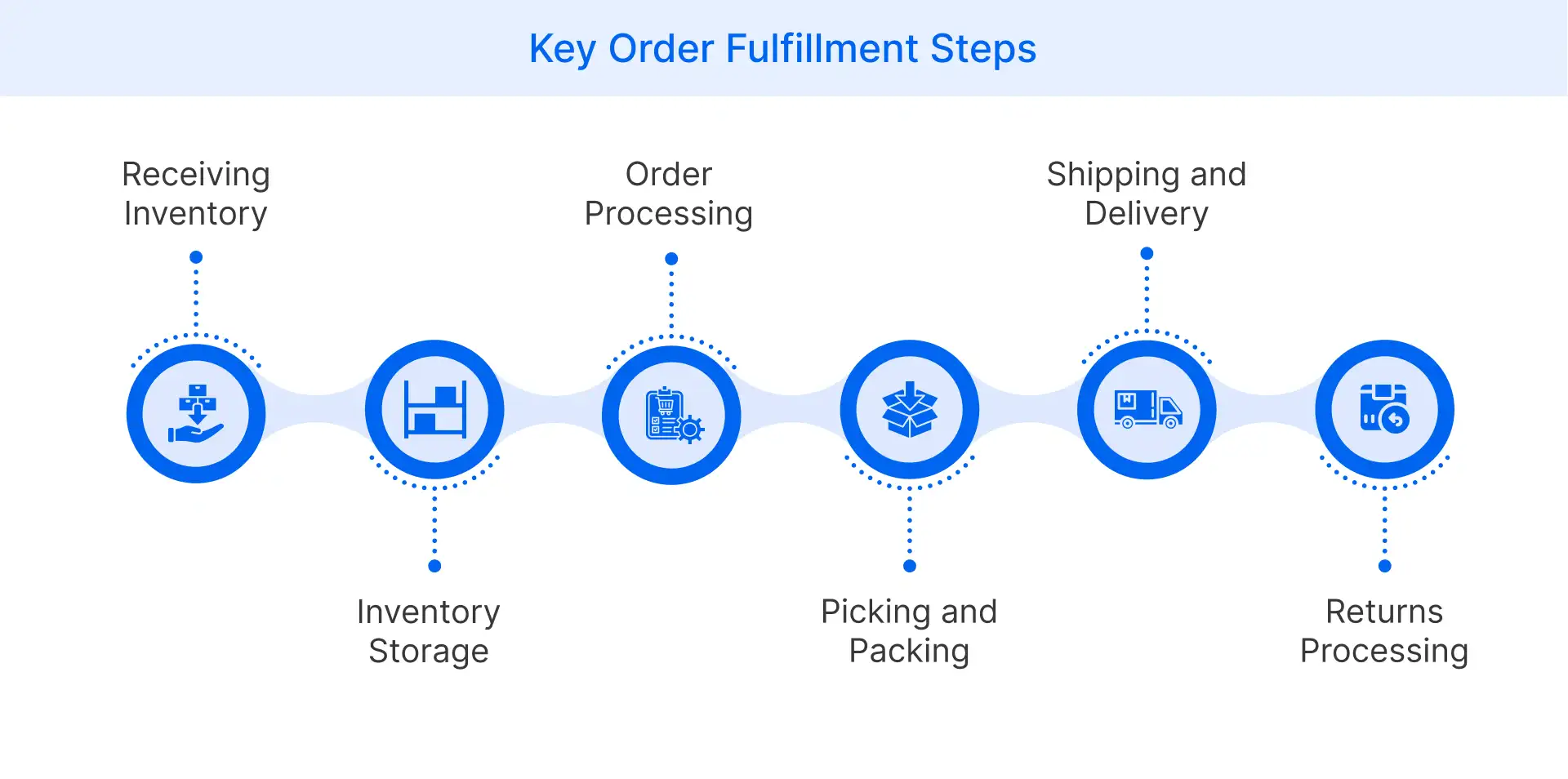
While the process may appear simple, effective order fulfillment plays a key role in modern supply chain management. From managing inventory levels to ensuring faster delivery times, each step significantly impacts the customer base and overall bottom line.
Understanding the significance of the entire order fulfillment process is essential for retail businesses seeking to thrive in today’s competitive marketplace.
Here is why it matters:
- Fast, accurate order delivery builds customer trust and encourages repeat purchases, driving long-term business success.
- Well-designed fulfillment operations cut unnecessary fulfillment costs while ensuring products flow smoothly from warehouse shelves to customers’ hands.
- Flexible fulfillment systems help businesses navigate growth phases and handle large order volumes without compromising service quality.
- Order data reveals valuable patterns about customer preferences, inventory needs, and shipping performance for smarter business decisions.
What are Order Fulfillment Centers?
Order fulfillment centers are specialized facilities designed to manage the storage, processing, and shipping of customer orders on behalf of retailers. Unlike traditional warehouses that mainly store bulk inventory, fulfillment centers handle dynamic operations focused on rapid order movement.
These centers receive goods from suppliers, sort them into organized storage zones, and manage inventory in real-time. When an order is placed, fulfillment staff pick the items, pack them securely, and prepare them for shipping using designated carriers.
The physical layout of an order fulfillment center is optimized for speed and accuracy. It includes designated zones for inbound shipments, inventory storage, packing stations, and outbound loading docks. Many centers also leverage automation tools such as barcode scanners, conveyor systems, and order fulfillment software to increase efficiency.
What are the Different Order Fulfillment Methods?
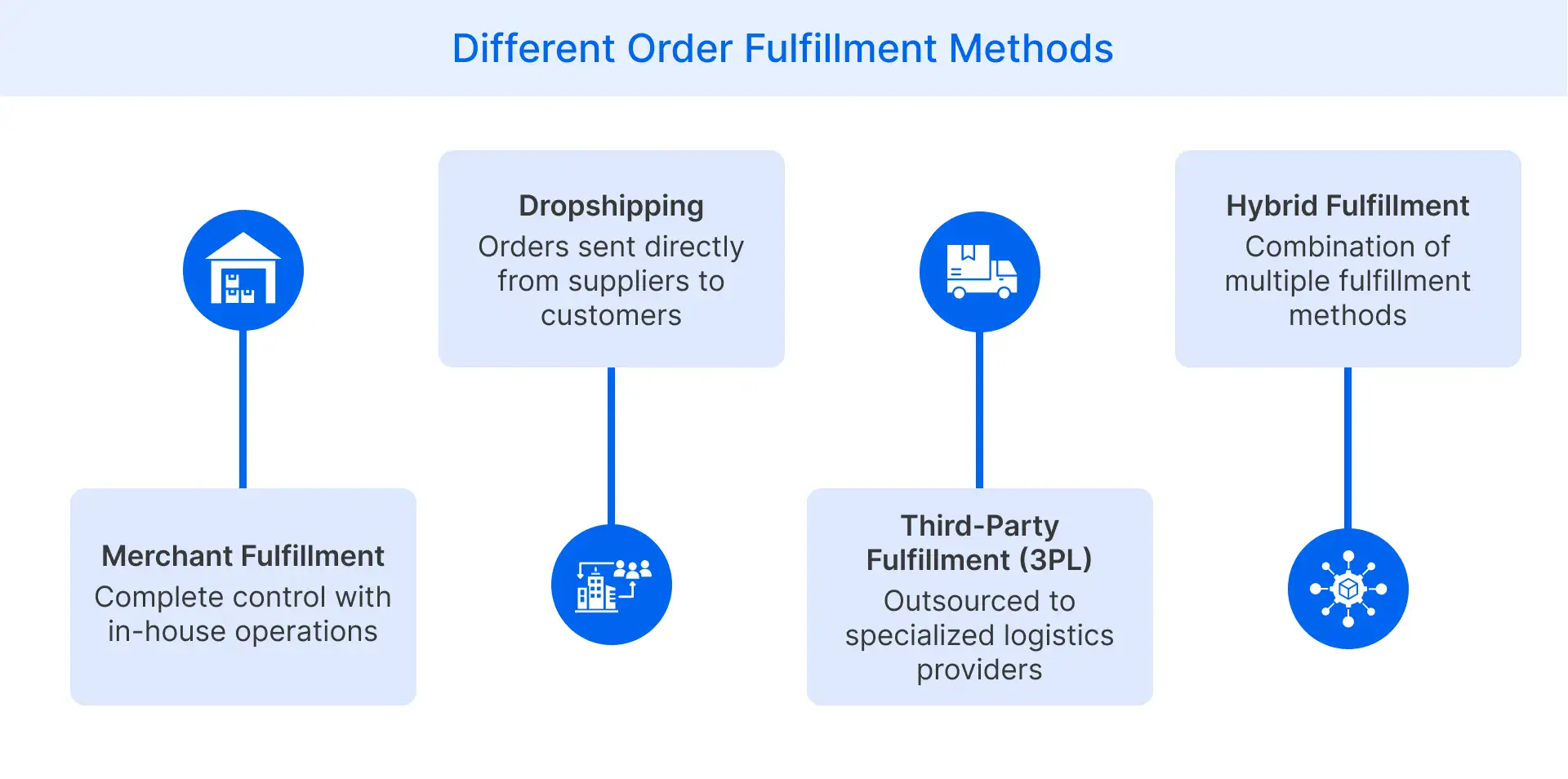
Retailers can choose from several distinct order fulfillment approaches, each offering unique advantages and limitations.
Merchant Fulfillment
In merchant fulfillment (also called in-house fulfillment), small businesses manage the entire order management process internally using their own warehouse space, equipment, and personnel. This approach gives businesses complete control over inventory management, quality standards, and the customer unboxing experience. Retailers using this method maintain direct oversight of operations while avoiding fees payable to an external order fulfillment company.
Dropshipping
Dropshipping eliminates inventory management responsibilities by allowing online marketplaces to transfer customer orders directly to suppliers or manufacturers. These partners then ship products directly to end customers under the retailer’s branding. This low-investment model requires minimal upfront capital and eliminates warehousing costs, making it ideal for new businesses testing product lines or expanding assortments.
Third-party Fulfillment
Third-party fulfillment involves outsourcing warehousing, picking, packing, and shipping operations to specialized logistics providers (3PLs). These companies offer infrastructure, technology, and expertise that would be costly to develop internally. Retailers benefit from professional order fulfillment service without capital investments in facilities, while gaining access to discounted shipping rates and established distribution networks.
Hybrid Fulfillment
Hybrid fulfillment combines multiple approaches to optimize order processing across different multiple sales channels. An online store might handle popular products in-house while dropshipping specialty items or use distribution center services for peak season overflow. This flexible strategy allows businesses to balance control and efficiency, especially when operating across multiple regions or managing diverse product catalogs with varying storage requirements.
How to Determine Your Order Fulfillment Strategy?
Selecting the optimal order fulfillment strategy requires careful evaluation of the following key factors:
- Business Type and Volume: Match your order fulfillment model to product types and order volume. High-frequency businesses may need automation, while low-volume models benefit from direct or hybrid approaches.
- Cost Structure and Resources: Evaluate warehousing, shipping, and staffing costs. Outsourcing may reduce overheads, while in-house fulfillment offers greater control but higher operational expenses.
- Location and Delivery Scope: Consider your delivery regions. Distributed fulfillment centers or 3PLs can help reduce transit time for national or international shipments.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Choose a model that adapts as your business grows. Fulfillment solutions should handle peak demand and product diversification without major disruptions.
What are the Best Practices to Improve Your Order Fulfillment Process?
Companies that excel in order fulfillment consistently apply the following best practices:
- Implement Real-Time Inventory Management: Businesses should deploy integrated inventory systems that provide visibility across all channels and locations. These solutions help manage stock levels and enable accurate order promising based on actual availability rather than estimated counts.
- Embrace Strategic Automation: Organizations can identify repetitive, labor-intensive tasks most suitable for automation technologies. Implementing conveyor systems, barcode scanners, automated sorting equipment, and robotic picking assistants significantly reduces processing times.
- Invest in Comprehensive Staff Training: Companies must develop structured training programs that cover standard operating procedures, equipment operation, and safety protocols. Regular skill development sessions ensure all team members understand their roles within the larger fulfillment ecosystem.
- Adopt Mobile Technology Solutions: Mobile devices equipped with warehouse management applications allow staff to access real-time information anywhere in the facility. These tools enable on-the-spot inventory checks, provide picking instructions, verify order accuracy, and capture shipment data.
- Establish Continuous Improvement Frameworks: Forward-thinking organizations implement systematic approaches to performance measurement and process refinement. Regular analysis of key metrics, structured problem-solving methodologies, and formal feedback loops drive ongoing operational enhancements.
Conclusion
Strategic order fulfillment represents a critical competitive differentiator in today’s retail environment, where customer expectations continue to rise. Businesses that thoughtfully design their fulfillment processes create significant advantages in customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and market responsiveness. By selecting appropriate fulfillment methods, implementing proven best practices, and proactively addressing common challenges, retailers position themselves for sustainable growth.
FAQ
Key performance indicators include order accuracy rates, on-time delivery percentages, order cycle time, cost per order, inventory turnover rate, and return rates. Companies should also monitor perfect order percentage, picking efficiency, shipping cost analysis, and customer satisfaction scores related to the delivery experience.
Modern fulfillment operations benefit from warehouse management systems, automated sorting equipment, picking technologies like voice-directed workflows, and predictive analytics tools. Cloud-based platforms integrate with e-commerce systems, while mobile scanning devices and IoT sensors provide real-time visibility throughout the fulfillment process.
Seasonal fluctuations create capacity challenges, requiring businesses to adjust staffing levels, storage space, and processing capabilities. Companies implement flexible resource allocation strategies, develop contingency plans for peak periods, and use historical data to forecast inventory needs during high-demand seasons.
Order fulfillment encompasses the entire process from receiving inventory to delivering products, including storage, processing, and returns handling. Shipping represents just one phase within the broader fulfillment workflow, focusing specifically on transporting packaged orders from fulfillment locations to end customers.

