Table of Contents
- What is Merchandising?
- What are the Key Elements of Merchandising?
- Types of Merchandising Techniques
- Benefits of Effective Merchandising
- Challenges in Merchandising
- What is Merchandising in Omnichannel Retail?
- How to Measure Merchandising Success?
- Conclusion
What is Merchandising?
Merchandising is the structured approach retailers use to present and promote products in ways that attract customers and drive sales. It ensures that the right products are available at the right time, place, and price, optimizing both in-store and online shopping experiences.
This process includes strategies such as product placement, visual displays, promotional pricing, and inventory management. In e-commerce, merchandising extends to website layout, personalized recommendations, and digital marketing tactics that influence customer behavior.
By implementing effective merchandising techniques, retailers can enhance customer engagement, improve conversion rates, and maintain a competitive edge.
What are the Key Elements of Merchandising?
Merchandising is built on several fundamental components that help retailers create an engaging shopping experience and drive sales.
- Product Presentation: How a product is displayed significantly impacts customer interest and sales. Organized shelves, strategic product placement, and clear signage help shoppers quickly find what they need. In e-commerce, high-quality images, detailed descriptions, and customer reviews enhance product visibility and influence purchase decisions.
- Pricing Strategy: Effective pricing ensures competitiveness while maintaining profitability. Retailers use strategies like discounts, bundling, and psychological pricing to attract buyers. Dynamic pricing, which adjusts prices based on demand and market trends, is becoming increasingly popular in digital merchandising.
- Inventory Management: Balancing supply and demand is critical to avoiding stock shortages or overstocking. Real-time inventory tracking ensures products are available when customers need them. Technologies like automated restocking and demand forecasting help retailers maintain optimal stock levels and improve merchandising efficiency.
- Visual Displays: Attractive in-store displays and well-designed digital interfaces enhance merchandise appeal. Window displays, end caps, and promotional setups encourage impulse buying in physical stores. Online, curated collections, banners, and interactive visuals create an engaging shopping experience.
Types of Merchandising Techniques
Here are the key merchandising techniques retailers use to maximize sales:
- Visual Merchandising: This technique focuses on the aesthetic presentation of products in physical stores. Well-designed window displays, attractive shelf arrangements, and strategic lighting create an engaging shopping experience that encourages impulse purchases.
- Cross-Merchandising: Placing complementary products together increases sales by encouraging bundled purchases. For example, displaying bread next to spreads or pairing electronics with accessories enhances convenience and boosts transaction value.
- Digital Merchandising: In e-commerce, digital merchandising involves optimizing website layouts, product recommendations, and search filters. High-quality images, engaging product descriptions, and AI-driven personalization improve customer engagement and conversion rates.
- Promotional Merchandising: Limited-time discounts, seasonal sales, and exclusive deals create urgency, driving higher sales. In physical stores, promotional displays highlight special offers, while online retailers use banners, pop-ups, and email campaigns to attract buyers.
- Category-Based Merchandising: Arranging products by category or theme helps shoppers find items easily. Supermarkets, fashion stores, and e-commerce platforms use this approach to improve navigation and enhance the overall shopping experience.
Benefits of Effective Merchandising
By effectively presenting products, retailers can create a seamless shopping experience that encourages repeat purchases and brand loyalty. Here are the key benefits of well-executed merchandising.
- Improved Customer Experience: A well-organized store layout and clear product displays help customers find items quickly. In e-commerce, intuitive navigation, personalized recommendations, and high-quality visuals enhance shopping convenience and satisfaction.
- Increased Sales and Revenue: Effective merchandising influences purchasing decisions through product placement, promotions, and appealing visual displays. By using cross-merchandising and limited-time offers, retailers can drive impulse purchases and boost revenue.
- Better Inventory Turnover: Proper merchandising ensures products are strategically displayed and stocked, reducing unsold inventory. Demand forecasting and data-driven insights help retailers manage stock levels efficiently and avoid overstocking or shortages.
- Strengthened Brand Perception: Consistent merchandising reinforces brand identity and trust. A well-maintained retail environment and cohesive online presentation establish a strong market presence, making customers more likely to choose your brand.

Challenges in Merchandising
While merchandising plays a crucial role in retail success, it comes with challenges that can impact efficiency and profitability.
- Space Constraints: Limited shelf or display space can restrict product visibility and assortment. Retailers must strategically allocate space, ensuring high-demand products are prominently displayed without overcrowding.
- Seasonal Demand Fluctuations: Merchandising strategies must adapt to shifting seasonal trends. Managing stock levels for peak and off-peak seasons requires accurate demand forecasting to prevent overstocking or stockouts.
- Omnichannel Integration: Aligning physical store merchandising with online strategies can be complex. Ensuring consistency in pricing, product availability, and promotions across multiple sales channels requires advanced planning and synchronization.
- Managing Changing Consumer Preferences: Customer expectations evolve rapidly, requiring retailers to update their merchandising strategies frequently. Staying ahead of trends, personalizing offerings, and leveraging data analytics help retailers adapt to shifting market demands.
What is Merchandising in Omnichannel Retail?
In omnichannel retail, merchandising has transformed into a cohesive strategy that integrates across all customer touchpoints. Retailers are now creating a unified brand experience across physical stores, e-commerce platforms, mobile apps, and social media channels. This approach ensures consistent product presentations, pricing, and promotions, regardless of the shopping channel.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and data analytics are instrumental in shaping modern omnichannel merchandising. These technologies allow retailers to analyze extensive customer data, predict trends, and personalize product recommendations in real-time. Automation aids in streamlining inventory management across channels, aligning product availability with demand. By utilizing these tools, retailers can develop dynamic merchandising strategies that adapt to evolving consumer behaviors and market conditions.
The essence of successful omnichannel merchandising lies in maintaining a unified view of inventory and customer interactions. This strategy enables services like buy-online-pickup-in-store (BOPIS) or ship-from-store, enhancing customer experience and optimizing inventory utilization across all channels.
How to Measure Merchandising Success?
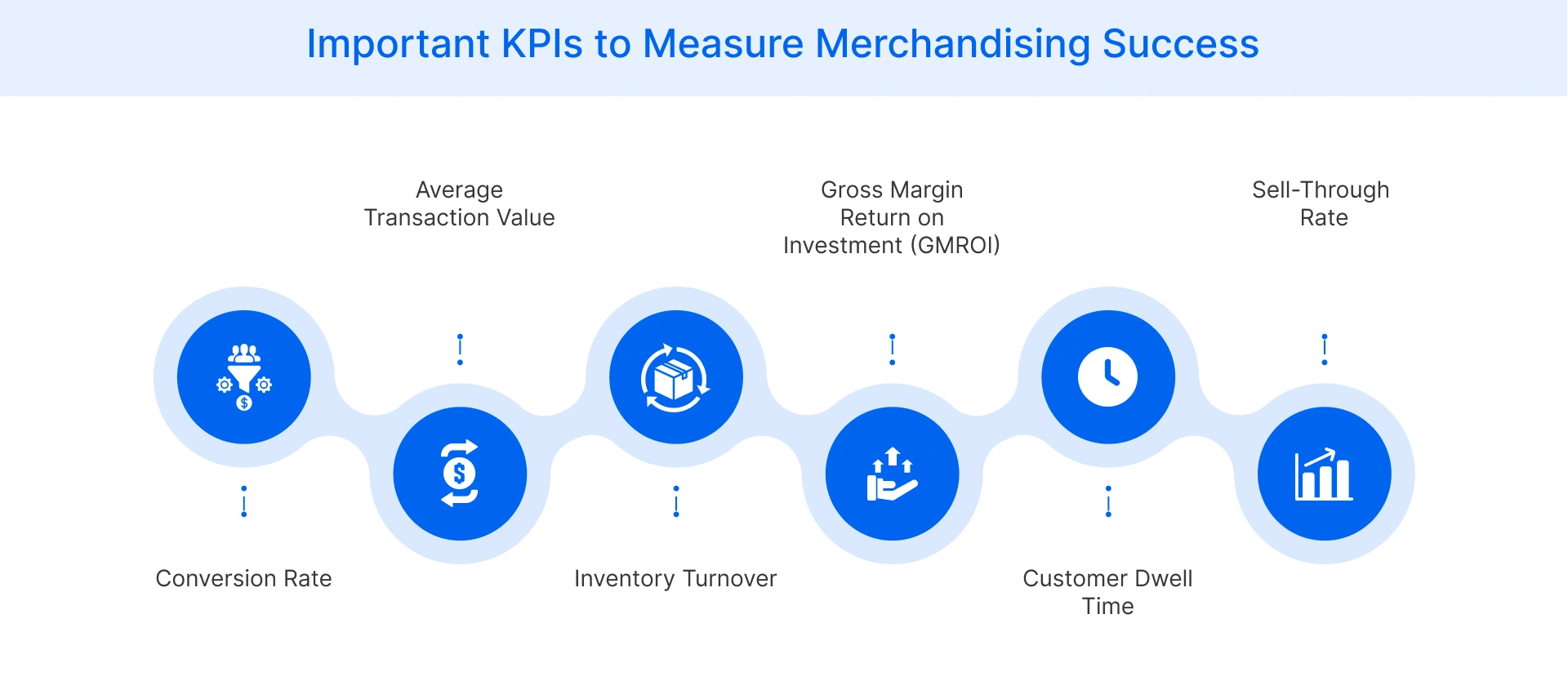
Evaluating the effectiveness of merchandising strategies requires tracking specific key performance indicators (KPIs):
- Conversion Rate: Measures the percentage of store visitors who make a purchase, indicating the effectiveness of merchandising in turning browsers into buyers.
- Average Transaction Value: This metric tracks the average amount spent per customer transaction, reflecting successful upselling and cross-merchandising efforts.
- Inventory Turnover: It calculates how quickly inventory is sold and replaced, indicating effective merchandising and stock management.
- Gross Margin Return on Investment (GMROI): This KPI measures inventory profitability by dividing gross margin by average inventory cost.
- Customer Dwell Time: Monitor how long customers spend in different store areas. Longer dwell times in key merchandising zones often correlate with higher sales.
- Sell-Through Rate: It measures the percentage of inventory sold within a specific period. Strong sell-through rates indicate effective merchandising and product demand.
Conclusion
Merchandising plays a crucial role in shaping customer experiences, optimizing inventory, and driving sales. Effective strategies, both in-store and online, ensure product visibility, competitive pricing, and seamless shopping journeys. By leveraging data analytics, automation, and omnichannel integration, you can enhance merchandising efficiency and adapt to evolving market demands. Implementing the right tools and techniques will help you maximize profitability, strengthen brand presence, and stay ahead in competitive markets.
FAQ
Yes, small businesses can improve the sale of products by applying merchandising techniques such as strategic product placement, attractive displays, and dynamic pricing. Digital tools, AI-driven recommendations, and customer insights enable small retailers to compete effectively with larger brands.
Retailers should update merchandising strategies regularly based on market trends, customer behavior, and seasonal demand. Frequent analysis of sales data, inventory turnover, and competitor pricing helps optimize product placement, promotions, and inventory management for maximum profitability.
Merchandising focuses on product presentation, pricing, and placement to drive sales, while marketing involves promoting products through advertising and branding strategies. Both complement each other, but merchandising directly influences in-store and online shopping experiences to optimize conversions.

