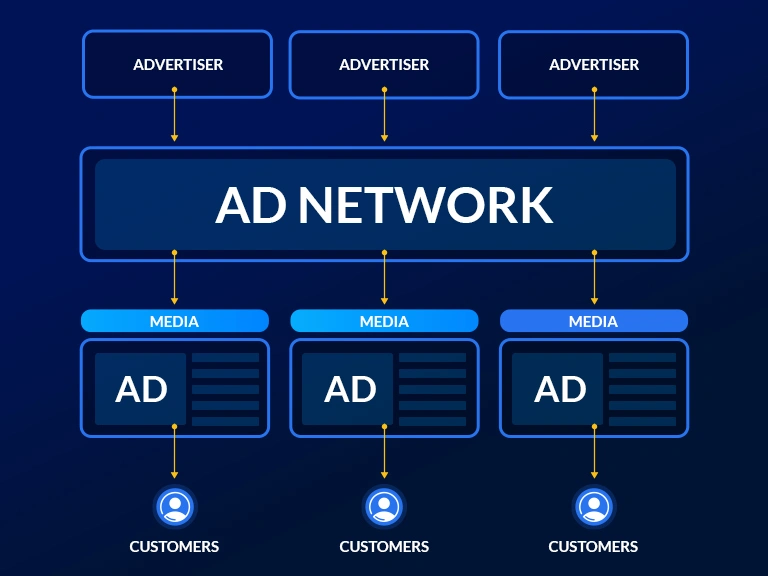
What is an Advertising Network?
As mentioned earlier, an advertising network, also known as an ad network, acts as a bridge between businesses seeking to advertise and publishers with digital space to offer, such as websites and mobile apps. In short, the setup is designed to make the most of available digital ad space by matching it with the needs of various advertisers. As a result, advertisers can reach their target audience while allowing publishers to monetize their remnant ad inventory.
Now, let’s explore the specific benefits that ad networks offer to publishers and advertisers, shedding light on why they are increasingly becoming a staple in digital marketing strategies.
Benefits of Ad Networks
Ad networks streamline the process of digital advertising and optimize outcomes for both publishers and advertisers. Here are the benefits they offer:
For Publishers
- Expanded Advertiser Access: By being part of ad networks, publishers get instant access to various advertisers. It is particularly beneficial for smaller publishers who might otherwise struggle to attract direct advertising deals.
- Monetization of unsold inventory: Ad networks provide an alternate avenue for publishers to monetize unsold inventory. However, the revenue generated from Ad Networks is unlikely to match the potential of direct ad sales.
A better option here is building a custom retail media platform, as it offers greater control and transparency. This is where Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC) emerges as an essential partner. FCC assists businesses in developing their own retail media platform by providing the intelligence and technology necessary to create a transparent, efficient advertising ecosystem.
For Advertisers
- Cost Efficiency: Ad networks provide various pricing models, such as CPM (Cost Per Mille) and CPC (Cost Per Click), enabling advertisers to select the most cost-effective strategy for their campaign goals.
- Access to Inventory from Publishers at Scale: Ad networks offer advertisers easy access to publisher inventory at scale. This extensive reach enables advertisers to feature their ads across diverse platforms and audiences. It is also helpful in expanding their market presence.
- Time-Saving: Ad networks streamline the advertising process, saving valuable time for advertisers. They automate the matching of ads with suitable publisher spaces and handle the crucial aspects of ad placement and negotiation. This efficiency allows advertisers to focus more on strategy and creative development than operational logistics.
- Better retargeting avenues: Ad networks keeps a close eye on customer’s previous purchases and allows advertisers to have better avenues for retargeting. With contextual advertising, it allows better ROI on digital advertising spend.
How Does the Ad Network Work?
Understanding the workings of an ad network is crucial for success in digital advertising. By breaking down the process into clear and sequential steps, we can gain a deeper insight into how these networks function. Let’s have a look at how digital ad networks operate:
Onboarding of Publishers
The first step involves the registration of publishers. Publishers specify details such as the type of ads they want to host, ad dimensions, and ad types. Sometimes, ad network providers also allow publishers to limit the pricing for the ad space.
Onboarding of Advertisers
Next, advertisers join the network by setting up an account where they define the details of their campaigns. This involves uploading ad creatives, setting budget limits, and specifying targeting parameters to attract the desired audience. Advertisers can choose from various ad formats supported by the ad network, ranging from display ads to video ads.
Ad Launch & Placement
Then, the ad server employs advanced algorithms to match advertiser campaigns with appropriate publisher inventory. This process considers factors like target audience, ad format, and content relevance. Once the match is made and ads are served on the publisher’s site, the ads are continually optimized based on real-time performance metrics. This phase underscores the nature of dynamic advertising, where ongoing adjustments are made to enhance visibility and engagement.
Ad Performance Tracking
Finally, both publishers and advertisers get access to detailed analytics provided by the network. These insights include metrics like impressions, clicks, and conversions, etc. The ability to track performance empowers advertisers to make data-driven decisions, maximizing the ROI of their campaigns. On the other hand, publishers can fine-tune their ad spaces for better effectiveness and revenue generation.
In the next section, let’s have a look at various pricing structures supported by Ad Networks:
Pricing Structures Offered by Ad Networks
Ad networks offer diverse pricing structures, catering to advertisers’ varying needs and goals. Here are the most popular pricing structures offered by ad network platforms:
- Cost Per Mille (CPM): This pricing model, where advertisers pay for every thousand impressions their ad receives, is ideal for campaigns aiming at high exposure. It’s particularly effective for brand awareness initiatives, where the focus is on reaching a wider audience base rather than immediate conversions.
- Cost Per Lead (CPL): Under CPL, advertisers are charged for each lead generated from their ads, such as a form submission or email sign-up. This model is perfect for campaigns where the main goal is conversion.
- Cost Per Click (CPC): In the CPC model, advertisers pay for each click their ad receives. This approach aligns advertising costs with user engagement, making it a popular choice for driving website traffic and gauging audience interest.
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA): CPA is a results-oriented model where advertisers pay only when a specific action, like a sale or a sign-up, is completed. It’s highly effective for campaigns focused on conversions and is a popular choice for direct response marketing.
- Budget Proportional View Share (BPVS): BPVS ensures equitable ad exposure relative to the advertiser’s budget. Exclusive to Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC), this model offers a level playing field, allowing all advertisers, regardless of budget size, to gain proportional visibility and opportunities.
Ad Targeting Capabilities Offered by Ad Network
Ad networks offer advanced targeting capabilities, enabling advertisers to reach specific audiences with precision, enhancing the impact and efficiency of their campaigns. Let’s investigate the varied ad targeting capabilities they offer:
- Demographic Targeting: This strategy involves segmenting audiences based on demographics like age, gender, income, education, and occupation. It allows advertisers to tailor their messages to resonate with a particular demographic group.
- Placement Targeting: Advertisers can choose specific websites or placements within a site for their ads. This ensures that ads are displayed in environments that align with the brand’s values and audience interests.
- Keyword Targeting: This involves targeting ads based on specific keywords related to the product or service. When users search for these keywords, or when they appear in the content they are viewing, the ads are displayed, increasing the likelihood of reaching interested parties.
- Contextual Targeting: Ads are matched with relevant site content, ensuring they appear in a contextually appropriate setting. This targeting is based on the subject matter of the web page, ensuring that the ad content aligns with user interests.
- Geographic Targeting: Advertisers can target ads to users based on their geographic location, from broad regions down to specific postal codes. This approach is particularly useful for localized marketing efforts or for businesses with a physical presence.
- Topic Interest Targeting: Ads are targeted to users based on their interests or the topics they frequently browse. This strategy ensures that ads reach users whose online behavior suggests an interest in the offerings.
- Remarketing: This strategy targets users who have previously interacted with the website or app. It enables advertisers to re-engage potential customers with an interest in their offerings.
Types of Ad Networks
Here are the various ad networks available for retail media experts:
Industry-Specific Ad Networks
These networks focus on specific industries or verticals, offering access to highly targeted audiences. For instance, a health-focused vertical ad network would connect advertisers with an audience deeply interested in health and wellness, making it an ideal option for healthcare companies. Such specialization ensures that marketing efforts are not broad but instead are deeply focused and relevant.
Premium Ad Networks
Premium ad networks are designed for brands aiming to place their ads on reputable sites, ensuring maximum visibility and enhanced brand prestige. These networks typically partner with elite publishers, offering premium ad slots that attract a sophisticated audience. This type of ad network is particularly advantageous for luxury brands or those seeking to associate with high-end content. An example of a premium ad network might include partnerships with internationally renowned news platforms and popular entertainment websites, providing advertisers with unparalleled exposure to an upscale audience.
Format-Specific Ad Networks
Specializing in particular ad formats, these networks cater to advertisers who prioritize certain content delivery types, such as interactive mobile ads or immersive video experiences. This specialization allows for targeted and effective advertising campaigns. Here, advertisers can select a network that excels in delivering the specific type of ad content they require. For instance, a network specializing in mobile ads would be perfect for a campaign targeting mobile app users. Likewise, a video ad network would suit advertisers aiming to capitalize on the engaging nature of video content.
Despite the prevalence of Ad networks, brands are rapidly shifting to building their own retail media platform due to the rapidly evolving digital ad space. More about this in our next section.
Why are Retailers Building Their Own Media Platform?
Retailers are increasingly turning toward building their retail media platforms, a trend powered by the impending deprecation of third-party cookies and the need to monetize their digital reach better.
Impact of Third-Party Cookie Restrictions
The traditional reliance on third-party cookies has been a vital aspect of digital advertising, powering targeted and measurable marketing campaigns. However, the digital advertising space is facing a paradigm shift due to Google’s decision to eliminate third-party cookies from Chrome by 2024 and several other privacy regulations. These include the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and state-level laws in the United States, such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), Virginia Consumer Data Protection Act (VCDPA), and Colorado Privacy Act (ColoPA). These changes are compelling retailers to rethink their strategies for targeting online shoppers. This situation demands innovative methods for data collection and ad targeting based on first-party data and privacy-compliant strategies.
Rise of Retail Media
In response to these challenges, retail media platforms are gaining prominence as an effective alternative. These platforms utilize first-party data and direct customer relationships, offering a new avenue for marketing. Retail giants such as Amazon, Tesco, and Walmart are at the forefront of this movement, leveraging the potential of retail media to generate revenue and establish stronger customer connections. Many other retailers are also coming on board with the concept of utilizing their digital space for third-party advertising.
However, it’s important to note that building a retail ad media platform is not that simple, it requires technological expertise. Hence partnering with a retail intelligence solution provider is recommended.
The following section will explore the benefits of forming technology partnerships in developing these networks.
Why Should You Seek Tech Partnership While Building Your Own Ad Network?
While building their own ad networks, retailers often encounter various challenges. One of the primary challenges is the complexity of ad tech infrastructure. Creating a successful ad network involves intricate technology for ad management, serving, tracking, and real-time keyword bidding processes alongside data analytics. For many retailers, the in-house development of such technology can be daunting, often requiring significant financial and temporal investment.
Partnering with retail media technology solution providers like Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC) offers a strategic advantage. With FCC Ads Manager, retailers can monetize their online assets and diversify retail revenue streams. Working with such tech partners offers retailers access to advanced ad tech infrastructure without the need for significant investment in development and maintenance.
Rather than relying solely on ad networks, it’s time brands start utilizing the technological expertise they need to excel. Want to know more about how we can help? Book a strategy call.