Table of Contents
- What is Price Stickiness?
- What Causes Prices to Become Sticky in Retail Markets?
- How Do Sticky Prices Differ from Flexible Prices?
- In What Ways Do Retailers Leverage Price Stickiness Strategically?
- Examples of Price Stickiness
- What Are the Implications of Sticky Pricing for Retailers’ Bottom Line?
- How Can Retailers Reduce Price Stickiness to Optimize Revenue?
- What Are the Key Triggers That Create Price Stickiness?
- What Challenges Do Retailers Face When Dealing with Sticky Pricing?
- How Does Price Optimization Software Help Overcome Price Stickiness?
- Conclusion
What is Price Stickiness?
Price stickiness refers to a situation where nominal prices remain unchanged even when market conditions suggest they should change. This means that even if supply, demand, or costs fluctuate, prices don’t always adjust immediately. Price stickiness is common in both traditional and digital retail environments as it influences how frequently companies revisit their pricing strategies and adapt to evolving market trends.
This resistance to change is a key concept in price stickiness, studied in macroeconomics. It plays a vital role in how retailers plan their pricing strategies and respond to market shifts:
- Sticky pricing can help preserve customer trust and perceived brand value during periods of economic instability.
- It can protect margins in markets where rapid price competition may damage brand positioning.
- It enables retailers to delay price changes until sufficient data supports a strategic pricing decision.
What Causes Prices to Become Sticky in Retail Markets?
Price stickiness in retail is shaped by a mix of economic costs, business practices, and consumer behaviors that discourage frequent price adjustments, such as:
- Menu costs refer to the expenses retailers face when updating prices across systems, platforms, and physical materials, making frequent price changes operationally and financially burdensome.
- Implicit contracts are unspoken agreements between brands and customers, where consistent pricing builds trust and frequent changes risk damaging long-term consumer relationships.
- Consumer psychology plays a significant role, as shoppers tend to associate stable prices with reliability, and sudden shifts may trigger hesitation or reduced brand loyalty.
- Internal processes often slow down price changes, particularly in large retail chains where pricing decisions must undergo multiple levels of approval and coordination.
- Competitive pressure can make businesses reluctant to be the first to increase prices, even when costs rise, to avoid losing customers to rivals with lower prices.
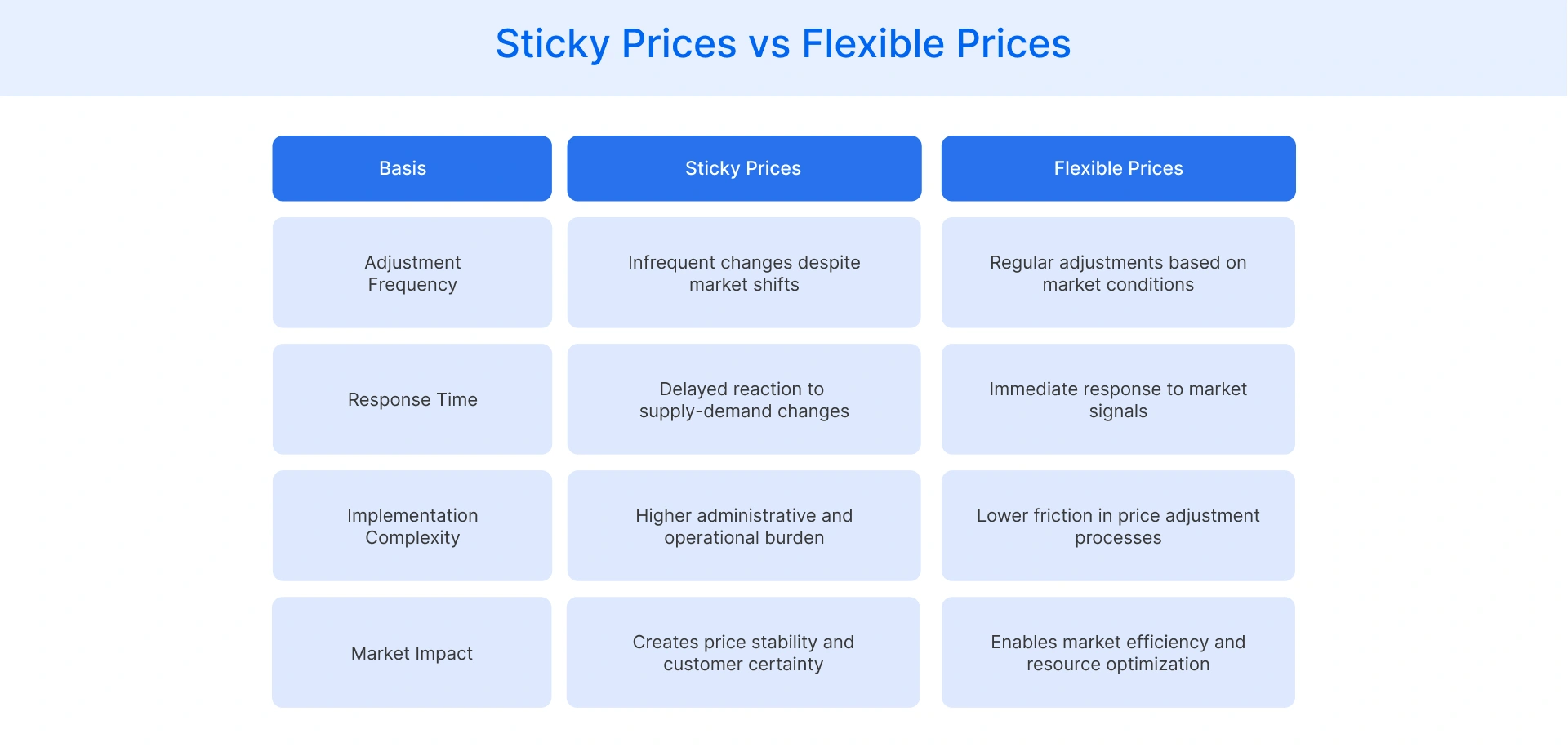
How Do Sticky Prices Differ From Flexible Prices?
Price stickiness and price flexibility represent opposite ends of the pricing adjustment spectrum in retail markets. While sticky prices remain constant despite changing economic conditions, flexible prices respond quickly and frequently to market forces like supply fluctuations, demand shifts, and competitive pressures.
Here are the key differences between these contrasting pricing approaches:
In What Ways Do Retailers Leverage Price Stickiness Strategically?
Retailers often choose to maintain steady prices as part of their business strategy. This approach can create several advantages when used correctly.
- Brand image building occurs when stores maintain stable prices to demonstrate that their products are of high quality. This helps customers view these products as worth paying a consistent price for, regardless of market fluctuations.
- Price point psychology is effective when retailers keep prices just below round numbers, such as $9.99 instead of $10. Customers become accustomed to these price points and view them as fair, making it more challenging to adjust them later.
- Customer trust development grows when shoppers can count on consistent pricing. When customers know what to expect price-wise, they are more likely to become repeat buyers and recommend the store to others.
- Standing out from competitors becomes possible when a retailer maintains stable prices, unlike others that constantly fluctuate. This helps stores avoid harmful price wars and instead focus on quality and reliability.
Examples of Price Stickiness
The following real-life examples illustrate how price stickiness operates in various business sectors and the strategies employed by companies to manage it.
- Coca-Cola kept its price at just 5 cents for an amazing 70 years (1886-1959) despite rising costs and economic changes. Instead of raising prices, they adjusted bottle sizes, which helped create one of the world's most recognized brands through consistent pricing.
- Costco's hot dog combo has stayed at $1.50 since 1985, becoming so important to their brand that former CEO Jim Sinegal strongly opposed any price rise. This famous example illustrates how maintaining a fixed price can become an integral part of a company's identity.
- Gas station prices tend to increase rapidly when oil costs rise, but decrease gradually when costs fall. This pattern illustrates how even competitive markets can exhibit one-sided price stickiness, influenced by customers' shopping and price comparison behaviors.
- Subscription services like Netflix and Amazon Prime maintain their monthly fees at a stable level for extended periods before making significant adjustments. This approach helps them manage increasing costs while avoiding small, frequent price changes that might cause customers to cancel.
What Are the Implications of Sticky Pricing for Retailers’ Bottom Line?
The aggregate price level in an economy is determined by how quickly different prices adjust across various sectors. In markets with greater nominal rigidity, the rate of inflation remains more stable but can create inefficiencies in resource allocation. This inherent stickiness in price adjustments has tangible consequences for businesses at the micro-level.
Price stickiness can limit a retailer’s ability to respond quickly to rising operational costs, potentially compressing profit margins and reducing overall financial flexibility. In inflationary environments, businesses that delay price increases risk absorbing additional costs, leading to lower short-term earnings.
From a revenue standpoint, sticking to fixed prices may result in missed opportunities. When demand surges or market conditions improve, retailers may struggle to capture additional value if prices remain unchanged. This can slow down revenue growth despite favorable market signals.
Sticky pricing also impacts competitive positioning. If competitors adopt more dynamic strategies, a retailer’s consistent pricing may appear outdated or less responsive. While it might build trust in the short term, it can erode market share if others innovate faster or offer better perceived value.
How Can Retailers Reduce Price Stickiness to Optimize Revenue?
Retailers can employ several strategic approaches to overcome price stickiness while maintaining strong customer relationships and maximizing revenue potential in a changing market environment.
- Incremental price adjustments involve making small, frequent changes rather than dramatic price shifts, helping customers adapt gradually to new price points while reducing the psychological impact that creates resistance to larger increases.
- Value bundling strategies enable retailers to effectively adjust the price-to-value ratio by combining products or adding services without altering the base price, thereby shifting customer focus from absolute price to the overall value proposition.
- Dynamic pricing technology enables retailers to implement data-driven price adjustments based on real-time factors, such as demand fluctuations, inventory levels, and competitive positioning, making price adjustments more responsive and strategically targeted.
- Customer communication frameworks enable retailers to explain necessary price changes through transparent messaging about cost increases or market conditions, thereby maintaining trust while educating customers about the factors necessitating adjustments.
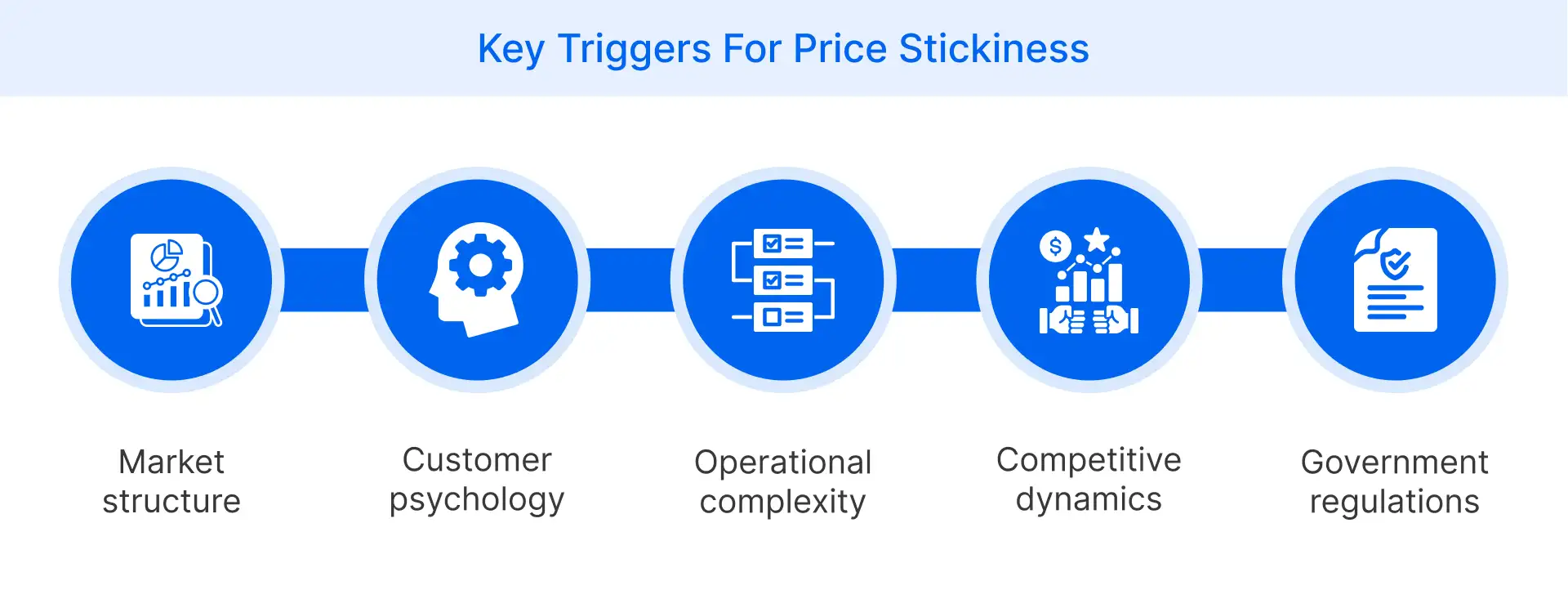
What Are the Key Triggers That Create Price Stickiness?
Price stickiness in retail arises due to a mix of structural, behavioral, and regulatory factors that influence how and when price changes are made.
- Market structure often limits flexibility, particularly in industries with high fixed costs or standardized pricing models that discourage frequent price adjustments.
- Customer psychology influences pricing decisions, as shoppers tend to prefer stable prices and may react negatively to frequent or unexpected price changes.
- Operational complexity delays price updates, particularly in large retail chains where multiple systems and approvals are involved in executing pricing decisions.
- Competitive dynamics increase hesitation, as retailers fear losing customers to rivals if they are the first to increase or decrease prices.
- Government regulations or pricing norms can restrict the frequency or extent of price changes, adding another layer of rigidity to retail pricing models.
What Challenges Do Retailers Face When Dealing With Sticky Pricing?
Retailers encounter several significant operational and strategic challenges when price stickiness prevents them from adjusting prices to reflect changing market realities.
- Profit erosion during cost inflation becomes inevitable when retailers are unable to pass on increased costs to consumers. This is particularly problematic for businesses with already thin margins, such as grocery stores and discount retailers.
- Missed revenue opportunities arise during periods of increased demand or reduced competition, when sticky prices prevent retailers from capturing additional value that customers would be willing to pay.
- Inventory management complications arise when prices cannot adjust to help clear excess stock or slow the depletion of scarce items. This could lead to holding costs or lost sales.
- Competitive positioning challenges arise when market leaders maintain high prices that smaller retailers feel compelled to match, despite lacking the same economies of scale or financial resources.
How Does Price Optimization Software Help Overcome Price Stickiness?
Price stickiness is a significant challenge for retailers due to a lack of timely data, the complexity of manual price adjustments, and uncertainty about customer response. Price optimization software provides an advanced solution by leveraging data analysis and artificial intelligence to enable dynamic and informed pricing decisions.
Here is how price optimization software helps businesses overcome price stickiness:
- Data-driven insights: The software analyzes sales, market trends, and competitor pricing to uncover customer behavior and price sensitivity, helping retailers identify when and where to adjust prices effectively.
- Dynamic pricing capabilities: It uses AI to adjust prices in real-time based on demand, competition, and inventory, enabling businesses to stay competitive and reduce delays caused by static pricing models.
- Personalized pricing strategies: By segmenting customers and assessing their willingness to pay, the software helps tailor pricing for different groups, maximizing revenue through targeted and customer-specific pricing.
- Streamlined and automated processes: It automates data analysis and pricing updates, reducing manual effort and error. This allows frequent price changes with lower costs and improved speed across all retail channels.
- Predictive modeling and scenario planning: The software simulates various pricing outcomes, enabling businesses to forecast performance, prevent pricing errors, and respond proactively to market changes before price stickiness becomes a problem.
By transforming complex data into actionable insights and enabling automated, dynamic adjustments, price optimization software enables retailers to navigate the challenges of price stickiness effectively.
Conclusion
Price stickiness plays a significant role in shaping retail pricing strategies. While it promotes stability and reinforces customer trust, it can also limit your ability to respond to changing market conditions. Understanding the causes, implications, and strategic uses of pricing allows retailers to make informed decisions. By combining consistent pricing practices with data-driven flexibility, you can maintain market relevance, protect margins, and build long-term profitability in competitive markets.
FAQ
Online retailers typically experience less price stickiness than physical stores due to lower menu costs and the ease of implementing changes. Digital platforms enable more dynamic pricing, whereas brick-and-mortar locations face higher operational barriers when adjusting price tags and signage.
Persistent inflation forces retailers to eventually overcome price stickiness despite resistance. Innovative businesses implement gradual increases rather than sudden jumps, communicate clearly about market conditions, and may adjust product sizes or compositions before changing established price points.
Price stickiness can strengthen loyalty programs by establishing stable reference prices, making reward discounts more meaningful. When base prices remain consistent, members perceive greater value in their program benefits, which enhances emotional connections and repeat purchase behavior.
Seasonal demand patterns create natural opportunities to adjust otherwise sticky prices. Retailers can implement new price structures during seasonal transitions when customer expectations reset, using promotional framing to introduce changes while maintaining perceived value.

