Table of Contents
- What is Purchase Price Variance (PPV) and How is It Calculated
- What Is Purchase Price Variance (PPV)?
- How is Purchase Price Variance Calculated?
- Favorable vs. Unfavorable Purchase Price Variance
- Example of Purchase Price Variance
- Factors that Influence Purchase Price Variance
- Why is Purchase Price Variance important?
- How to ensure that the Purchase Price Variance remains under control?
- Enhancing Profitability Through Intelligent Pricing
What is Purchase Price Variance (PPV) and How is It Calculated?
Retailers often set a strict budget for the quarter and expect their margins to remain safe until the invoice arrives. However, unexpected costs can quickly derail financial planning and reduce overall profitability if the variance is not monitored closely.
These shifts create gaps in financial planning, complicating buying decisions. The purchase price variance is the primary tool for analyzing these discrepancies and aligning actual costs with the original budget. It helps retailers anticipate higher costs by improving variance analysis and ensuring accurate procurement processes.
- Purchase price variance helps retailers identify spending inefficiencies in supply chain management while highlighting discrepancies between budgeted and actual costs.
- Monitoring PPV allows for quicker corrective action when prices fluctuate and ensures that companies can control costs effectively.
- Understanding these variances is essential to maintain healthy profit margins and streamline operations within procurement and finance teams.
- This metric allows businesses to evaluate supplier performance and helps them make informed decisions regarding future financial planning.
What Is Purchase Price Variance (PPV)?
Purchase Price Variance represents the difference between the standard price initially expected to be paid and the actual price ultimately paid. This financial metric is a critical tool for precisely measuring how procurement spending deviates from the original plan established by finance teams.
Retailers treat PPV as an important metric that supports cost accounting. It helps them understand whether the purchasing team negotiated a lower price or encountered higher costs due to market shifts. This insight supports corrective action across procurement teams and finance teams.
How is Purchase Price Variance Calculated?
Calculating this metric is a simple process when accurate data regarding direct material purchases and established standard costs is available.
The following three components help quantify the difference before you apply the formula:
- Actual Price: This is the final invoice amount per unit paid to the supplier including any applicable surcharges or discounts. It reflects the actual cost incurred by the business for acquiring the specific goods.
- Standard Price: This is the standard purchase price that finance teams agreed upon during the budgeting phase. It acts as the benchmark against which the actual invoice amount is compared to find the gaps.
- Actual Quantity: This figure represents the total number of units or volume of goods bought during the specific financial period. It is critical to use the exact quantity received to ensure the variance analysis is precise and actionable.
You can calculate PPV using the following formula:
PPV = (Actual Price – Standard Price) × Actual Quantity
The formula shows that even a minor price difference can significantly affect total spending when the number of units is high. It highlights whether you experienced a positive or negative variance in purchasing decisions.
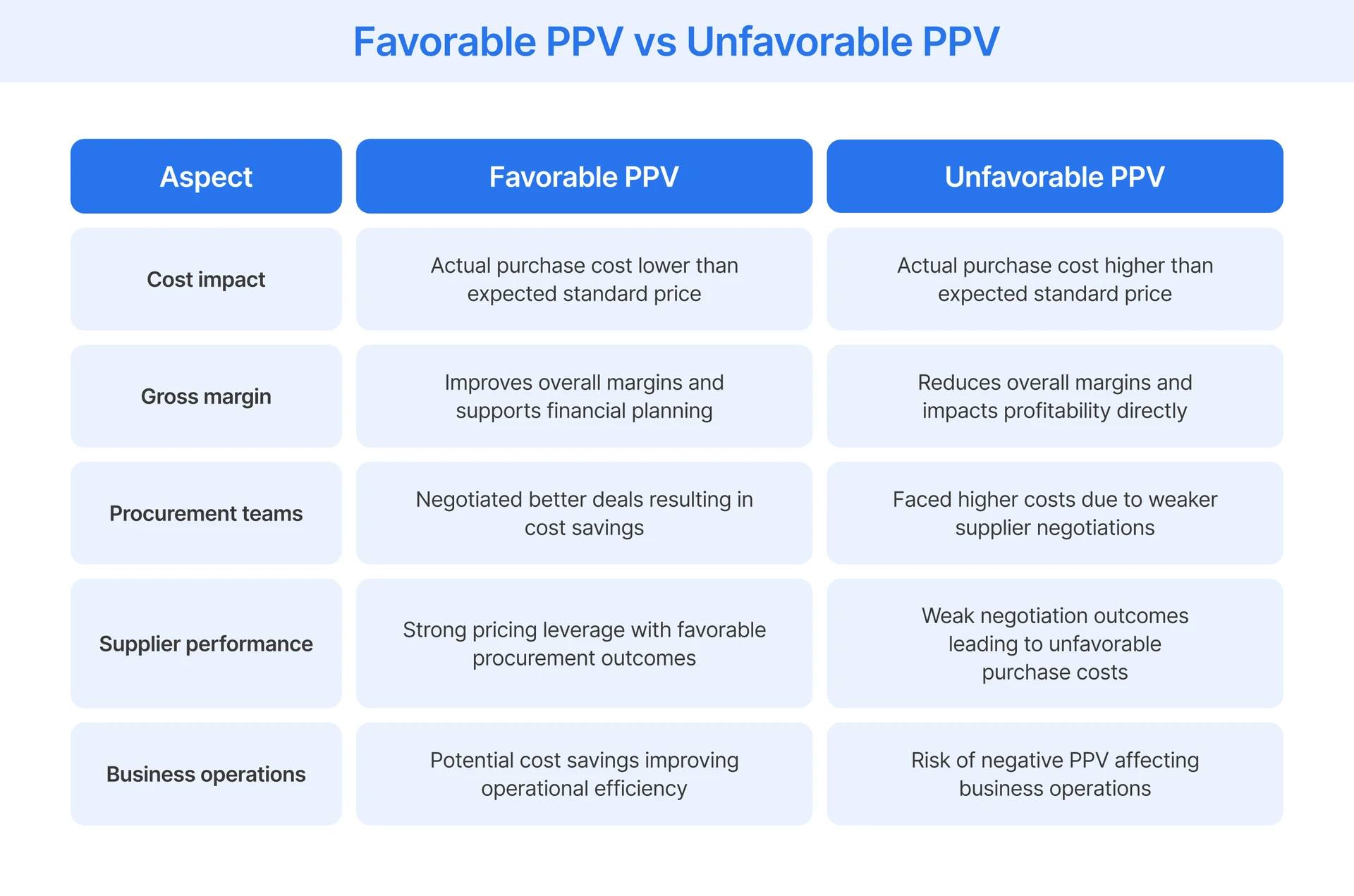
Favorable vs. Unfavorable Purchase Price Variance
Understanding the direction of the variance is crucial for maintaining a healthy gross margin and accurate cost accounting records. A price variance can go two ways and distinguishing between positive variance and negative variance is essential for success.
- Favorable Variance: A favorable variance occurs when paying less than expected, such as budgeting 10 dollars but paying only 8 dollars. While this results in cost savings, retailers must ensure that paying a lower price does not mean receiving junk.
- Unfavorable Variance: An unfavorable variance happens when paying more than expected and this directly eats into the gross margin and profitability. This negative outcome indicates higher costs than anticipated and is often due to supply chain disruptions or poor supplier performance.
Example of Purchase Price Variance
Here is an example to understand how purchase price variance works in real-world situations.
Imagine you are sourcing 1,000 smartwatches for an e-commerce store, with a standard cost of $50 per watch. However, supply chain issues hit unexpectedly and led to an actual cost of $55 per watch.
To calculate the variance, subtract the standard price from the actual price, then multiply by the number of units. In this case, the result is $(55 - 50) × 1,000 = $5,000.
This means you have an unfavorable price variance of $5,000. The PPV data indicate reduced margin and signal the need for stronger forecasting accuracy.
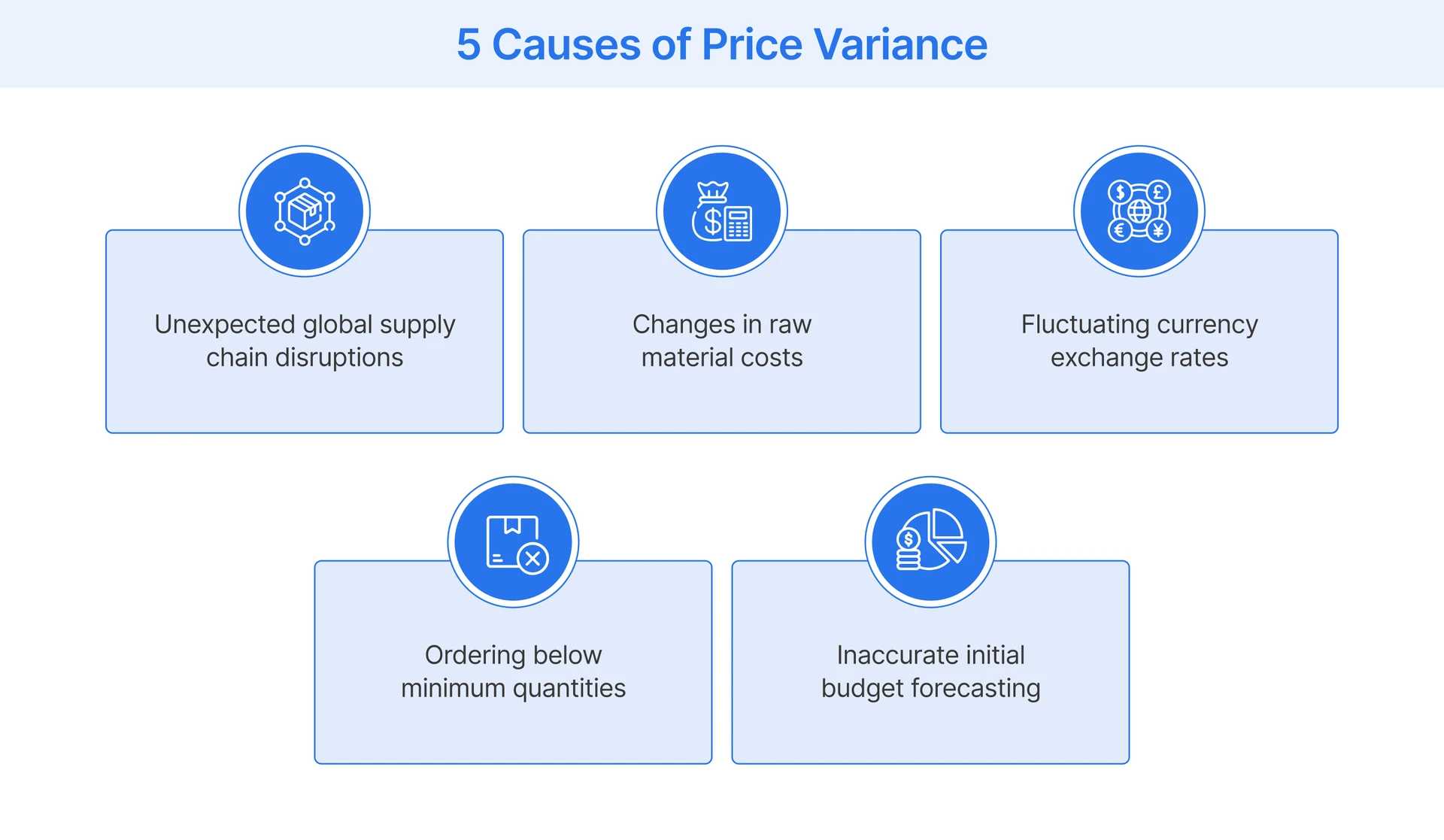
Factors that Influence Purchase Price Variance
Several external and internal elements can cause the purchase price to deviate significantly from the original financial plan.
- Supply and Demand: Material shortages or high demand can increase prices of goods rapidly when raw materials become scarce globally. This market pressure forces companies to pay above the standard price, negatively impacting the procurement budget.
- Market Fluctuations: Changes in the overall market can cause prices to rise or fall due to global economic conditions. Market shifts directly impact supplier performance and require monitoring these trends closely to anticipate sudden price changes.
- Supplier Pricing: Changes in a supplier pricing structure or negotiation outcomes can drastically affect procurement costs and variance. If a vendor updates their price list, the standard purchase price becomes outdated, leading to unfavorable purchase price variances.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Events like extreme weather or political shifts can impact costs significantly by causing delays or requiring expensive rerouting. These disruptive scenarios almost always result in higher costs for retailers and create significant challenges for supply chain management.
- Forecasting Accuracy: Poor forecasting can lead to a discrepancy between the standard and actual price if demand is miscalculated. Underestimating demand might lead to lost volume discounts, minimizing the risk of excess inventory but raising unit costs.
- Order Quantity: Ordering below minimum order quantities often triggers higher unit costs because suppliers typically offer better rates for larger batches. Failing to meet these specific thresholds results in a negative variance and reduces the efficiency of business operations.
- Quality Requirements: Switching to higher-quality materials increases the actual purchase cost while improving the final product for customers. While this improves the product, it negatively impacts PPV data and requires balancing quality with budgeted cost.
Why is Purchase Price Variance important?
Tracking this metric enables retailers to maintain financial health and operational efficiency while protecting the bottom line.
- Budget Management: It helps identify where actual costs exceed the budget, so finance teams can adjust allocations immediately. By identifying these gaps early, companies ensure capital is not wasted on unfavorable price variance and improve financial planning.
- Performance Evaluation: It serves as a key metric for evaluating the effectiveness of the purchasing team and the success of negotiation strategies. A consistent favorable variance suggests strong negotiation skills, while frequent losses may indicate a need for training or process improvement.
- Inventory Accuracy: Ensures inventory values are recorded correctly to prevent discrepancies in asset valuation. Accurate cost accounting prevents errors in financial reporting and reduces the risk that excess inventory valuation will affect the balance sheet.
- Strategic Decision-Making: Data derived from variance analysis helps improve the sourcing strategies and decide whether to switch vendors. This leads to long-term cost savings and allows businesses to maintain stability even when market conditions remain volatile.
- Profitability Analysis: It directly impacts the gross margin and net bottom line by revealing the actual cost of goods sold. Understanding price variance helps protect profit margins and allows retailers to adjust the selling price to compensate.
- Supplier Relationship Management: It highlights which suppliers consistently offer stable pricing versus those with volatile pricing structures or frequent rate hikes. Identifying reliable partners improves long-term supplier performance and reduces the risk of unexpected cost increases.
How to ensure that the Purchase Price Variance remains under control?
Retailers can implement specific strategies to minimize discrepancies and protect their margins from unexpected market fluctuations effectively.
- Better Forecasting: Do not just guess the standard price; use data effectively to predict future trends and market shifts. Leverage historical PPV data to align the standard cost closer to market reality and improve overall financial forecasting.
- Lock in Contracts: Negotiate fixed prices for six to twelve months to protect the business from sudden market shifts and inflation. Long-term agreements are among the best practices in procurement, providing stability for financial planning.
- Diversify Suppliers: Do not be held hostage by one vendor price hike or a sudden shortage of raw materials. Maintaining multiple sources keeps competition alive and this strategy often secures a lower price or favorable PPV for the business.
Enhancing Profitability Through Intelligent Pricing
Retailers can track cost variances diligently, but failing to act on them effectively is essentially watching money evaporate. This is where we at Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC) intervene to safeguard your growth and protect margins using data-driven precision.
When purchase prices fluctuate, your selling strategy needs agility to maintain a competitive edge without eroding margins. Our Pricing Manager leverages advanced ML-powered intelligence to translate these cost changes into optimal pricing actions across your entire assortment in real-time.
We use granular demand elasticity modeling to predict customer behavior and optimize prices throughout the product lifecycle. This approach ensures that you maximize profitability and clear inventory efficiently even when facing complex and unfavorable variance challenges in the market.
Our platform lets you simulate pricing scenarios to understand financial impacts before automating decisions in workflows. We transform price variance challenges into opportunities for smarter revenue management and give you precise control over your pricing strategy execution.
FAQ
Retailers should track purchase price variances monthly to ensure financial data remains current. Monthly tracking allows procurement teams to spot trends early and ensures that corrective action is taken before quarterly reports. Consistent monitoring is crucial for financial health and helps prevent long-term budget overruns.
Purchase price variance tracks the cost difference at the point of purchase when goods are initially acquired. Materials price variance refers to the cost difference when materials are used in manufacturers' production processes. Retailers focus on PPV to monitor procurement efficiency, while manufacturers track material price variance to control production costs.
PPV measures the difference in cost per unit between the standard price and the actual price paid. Purchase volume variance measures the difference between the number of units purchased and the quantity initially planned. PPV focuses on price changes and costs, while volume variance looks at quantity discrepancies and demand planning.
A favorable purchase price variance occurs when the actual price is lower than the budgeted standard price. It indicates cost savings for the company and usually results from bulk discounts or effective purchasing team negotiation. This positive variance improves the gross margin and directly contributes to overall profitability.

