FAQ
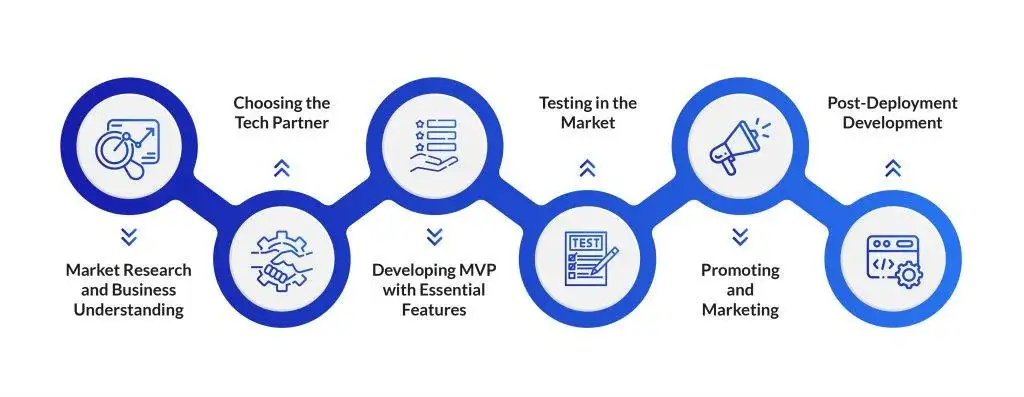
An MVP marketplace, or Minimum Viable Product marketplace, is the most basic, functional version of a multi-vendor platform launched with only the essential features required to facilitate the core transaction between a buyer and a seller to validate the central business idea. Its primary purpose is to efficiently test market demand and product-market fit.
MVP stands for Minimum Viable Product, and it works by creating and launching a version of a new product with just enough features to satisfy and be functional for early customers and to prove the product's core value proposition. The system operates on a continuous loop of Build-Measure-Learn: you launch the basic product, collect validated learning and feedback from real users, and then use that data to iteratively guide the next phase of development with minimal initial resource expenditure.
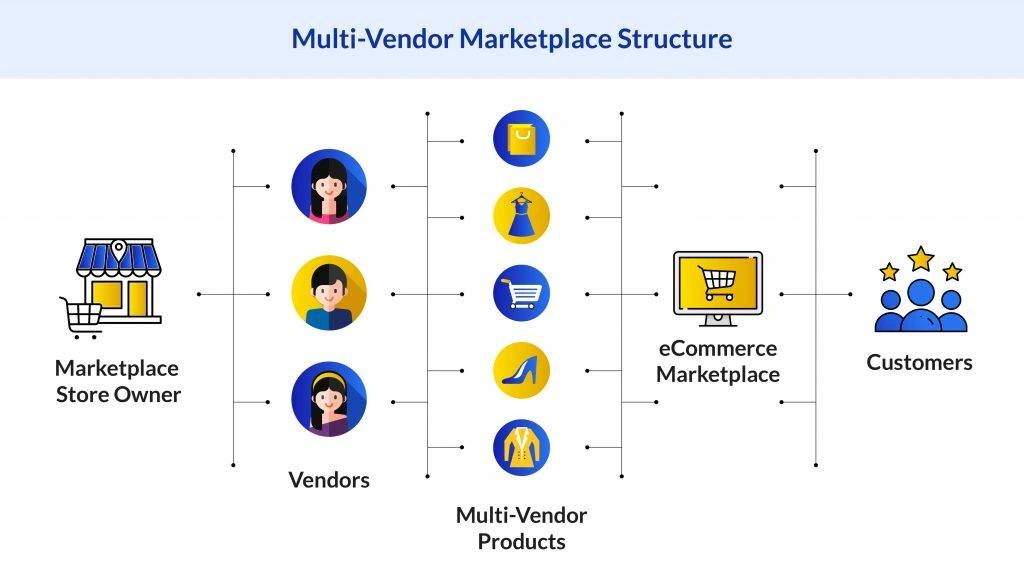
An example of a multi-vendor strategy is the parallel multi-vendor model, where a business procures the same or very similar products or services from several different suppliers simultaneously to diversify its supply chain and reduce risk. This strategy introduces competition among the vendors, which can lead to cost optimization, better quality, and increased leverage in negotiations for the marketplace operator.
The cost to build a multi-vendor marketplace varies widely based on the chosen development approach, with a basic MVP typically ranging from $40,000 to $80,000 if custom-built. A full-scale, intelligent marketplace with advanced features, mobile applications, and complex integrations can easily exceed $250,000 to $300,000, with final costs depending heavily on feature complexity, the technology stack, and the geographic location of the development team.
The difference between an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) and an MMP (Minimum Marketable Product) is primarily in their scope and purpose: the MVP is the leanest version focused on learning and validation of the core idea, often with basic design and limited functionality, used to test hypotheses. The MMP, however, is a later iteration that has a more complete set of features, an attractive design, and is polished enough to be genuinely marketable and sellable, focused on providing a complete user experience to a broader audience.
The purpose of the MVP is to achieve validated learning about customers and the market opportunity by getting a working product into the hands of early users as quickly as possible. This approach minimizes the wasted time and resources that would be spent building a full product based on incorrect assumptions, allowing the business to pivot or persevere based on real-world customer behavior and feedback.
A multi-vendor marketplace is an ecommerce platform where multiple independent third-party sellers can list and sell their products to customers, while the marketplace operator manages the technology infrastructure, facilitates the transactions, and handles core services like secure payment processing. Crucially, the platform operator does not own the inventory but earns revenue through commissions, fees, or subscriptions charged to the participating vendors.
Yes, Amazon is a multi-vendor marketplace, operating under a hybrid business model where it functions both as a direct first-party retailer selling its own inventory and as a marketplace platform hosting millions of third-party sellers.
Yes, you can build a multi-vendor marketplace on Shopify by using a third-party multi-vendor marketplace apps available in the Shopify App Store.
More Blogs
See how retailers and brands are winning with FCC

Everything About Price Skimming Strategy Explained
Read More
What is a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
Read More
Ultimate Guide To Dynamic Pricing Strategy In 2026
Read More
Retail Pricing Strategies: Winning with Promotion Pricing in Competitive Markets
Read More
Ad Tags: Enhancing Ad Serving Efficiency in Large-Scale Campaigns
Read More