FAQ
Dynamic pricing is often machine learning, as dynamic pricing is a strategy, while machine learning is a tool used to execute that strategy with high efficiency and complexity. Basic forms of dynamic pricing can rely on simple rules, but the most sophisticated systems, especially those available from platforms like FCC, leverage machine learning algorithms to process vast amounts of real-time data on demand, competitor prices, and inventory to predict optimal pricing and make instantaneous, automated adjustments.
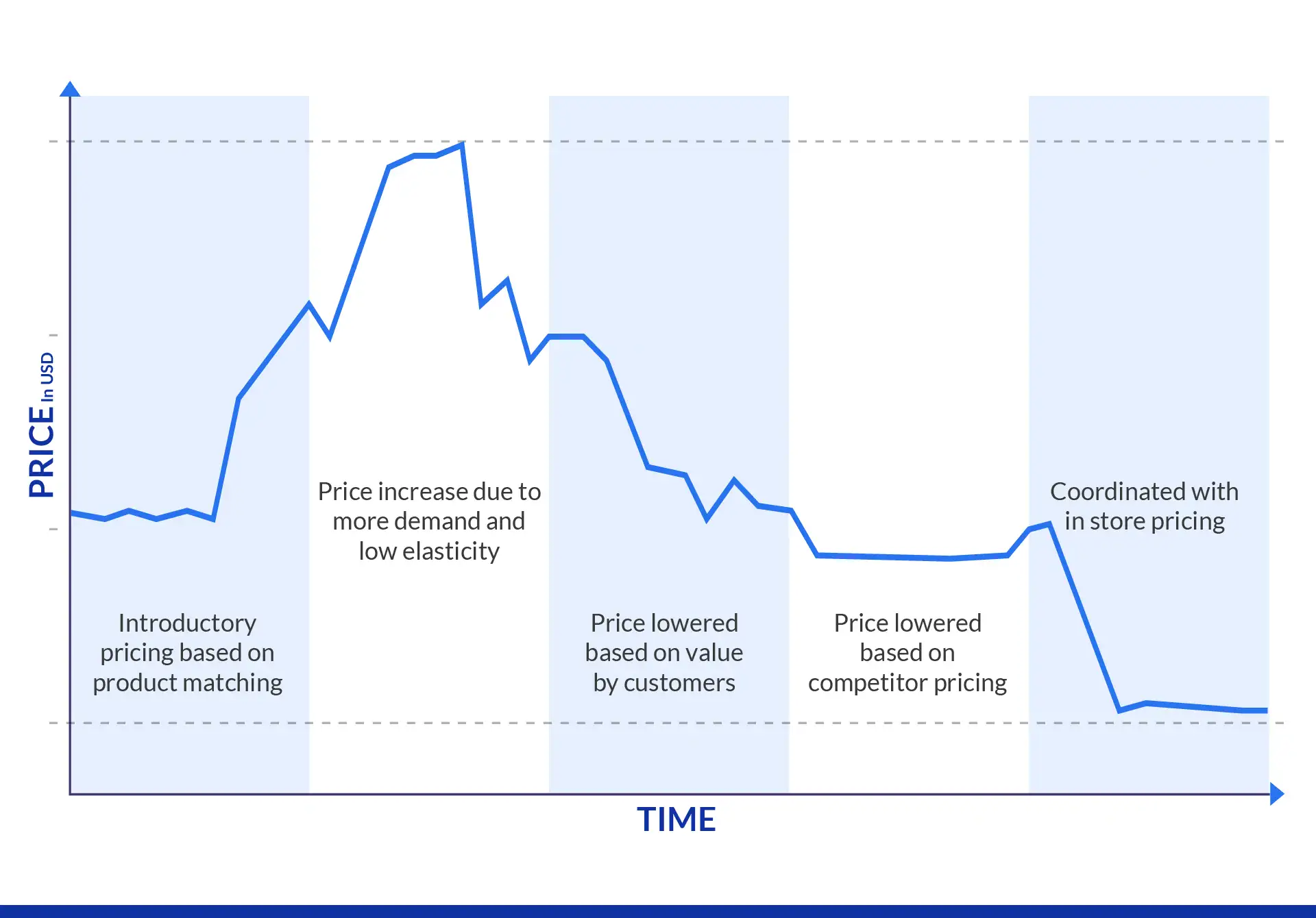
The dynamic pricing method is a flexible pricing strategy where the cost of a product or service is adjusted in real-time or near real-time in response to current market demand, supply levels, competitor actions, and specific customer conditions. This method moves away from static pricing to continuously capture the maximum possible revenue by ensuring the price always aligns with the current market valuation and perceived value.
Dynamic pricing involves employing AI capabilities, particularly machine learning, to analyze complex, multivariate data sets, including historical sales, seasonal trends, and live competitor information to predict consumer price elasticity and calculate the ideal price point for any given moment. AI automates this sophisticated decision-making process, allowing prices to be updated automatically and frequently across a large product catalog without human intervention.
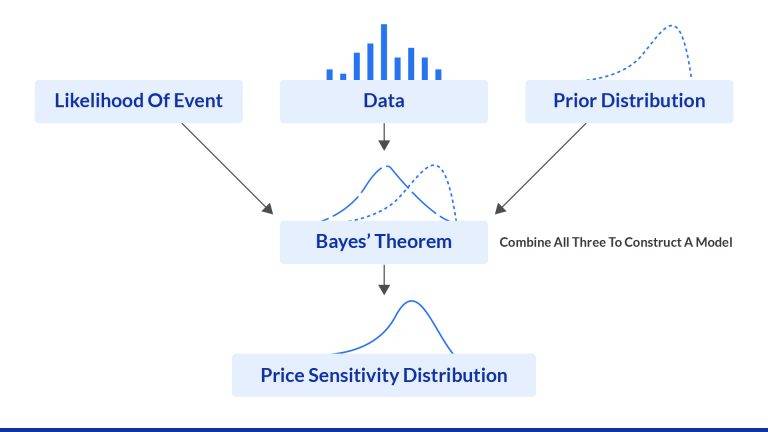
The machine learning model for pricing is typically a regression or classification algorithm trained on historical transaction data and market variables to predict the optimal price that will maximize revenue or profit for a given product at a specific time. This model learns the non-linear relationship between price, demand, and various external factors, allowing it to forecast the impact of a price change before it is implemented.
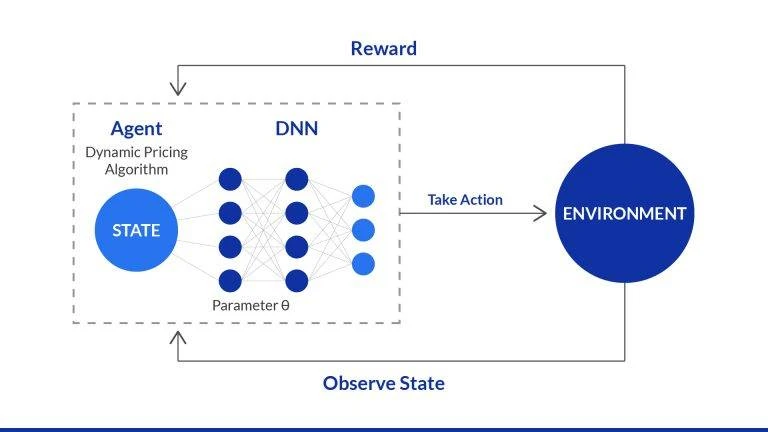
Dynamic programming in machine learning is an optimization technique used in some algorithmic problems to solve complex problems by breaking them down into simpler, overlapping subproblems and storing the results of those subproblems to avoid re-computation. While it is a computer science concept separate from machine learning itself, it is sometimes used within certain machine learning frameworks, such as in reinforcement learning, to calculate optimal sequences of decisions efficiently.
More Blogs
See how retailers and brands are winning with FCC

Everything About Price Skimming Strategy Explained
Read More
What is a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
Read More
Ultimate Guide To Dynamic Pricing Strategy In 2026
Read More
Retail Pricing Strategies: Winning with Promotion Pricing in Competitive Markets
Read More
Ad Tags: Enhancing Ad Serving Efficiency in Large-Scale Campaigns
Read More