Table of Contents
- What is B2C Commerce?
- How B2C Commerce Works?
- B2C vs B2B Commerce: Key Differences
- Key Features of B2C Commerce
- Types of B2C Commerce Models
- Advantages of B2C Commerce
- Challenges in B2C Commerce
- Conclusion
What is B2C Commerce?
B2C commerce refers to the process where businesses sell products or services directly to individual consumers, often through digital platforms. It covers everything from online shopping websites and mobile apps to physical retail stores offering direct purchases.
The evolution of digital technology has transformed B2C commerce, enabling small businesses to reach customers globally while providing seamless shopping experiences. E-commerce platforms, in particular, play a significant role by offering user-friendly interfaces, secure payment gateways, and personalized recommendations.
How B2C Commerce Works?
B2C commerce operates through a streamlined process where businesses sell products or services directly to consumers, facilitated by both online and offline channels. This business model involves multiple stages, from product discovery to final purchase, ensuring a smooth journey for shoppers.
In an online setting, customers browse products through websites, mobile apps, or social media platforms. E-commerce platforms act as virtual storefronts, allowing online retailers to showcase their own products with detailed descriptions, images, and pricing. Advanced platforms frequently integrate API functionalities and use JavaScript frameworks to build dynamic storefronts that respond in real time via robust server technologies.
Once customers select their desired items, they proceed to checkout, where digital payment methods play a crucial role. Credit cards, digital wallets, bank transfers, and buy-now-pay-later options offer flexibility, ensuring a seamless transaction experience. These methods not only enhance convenience but also improve security by protecting sensitive information.
Offline B2C commerce follows a similar journey but occurs in physical stores. Customers explore products in person, receive assistance from sales representatives, and complete purchases using cash, card, or mobile payment apps. While the setting differs, the focus remains on delivering a hassle-free buying experience.
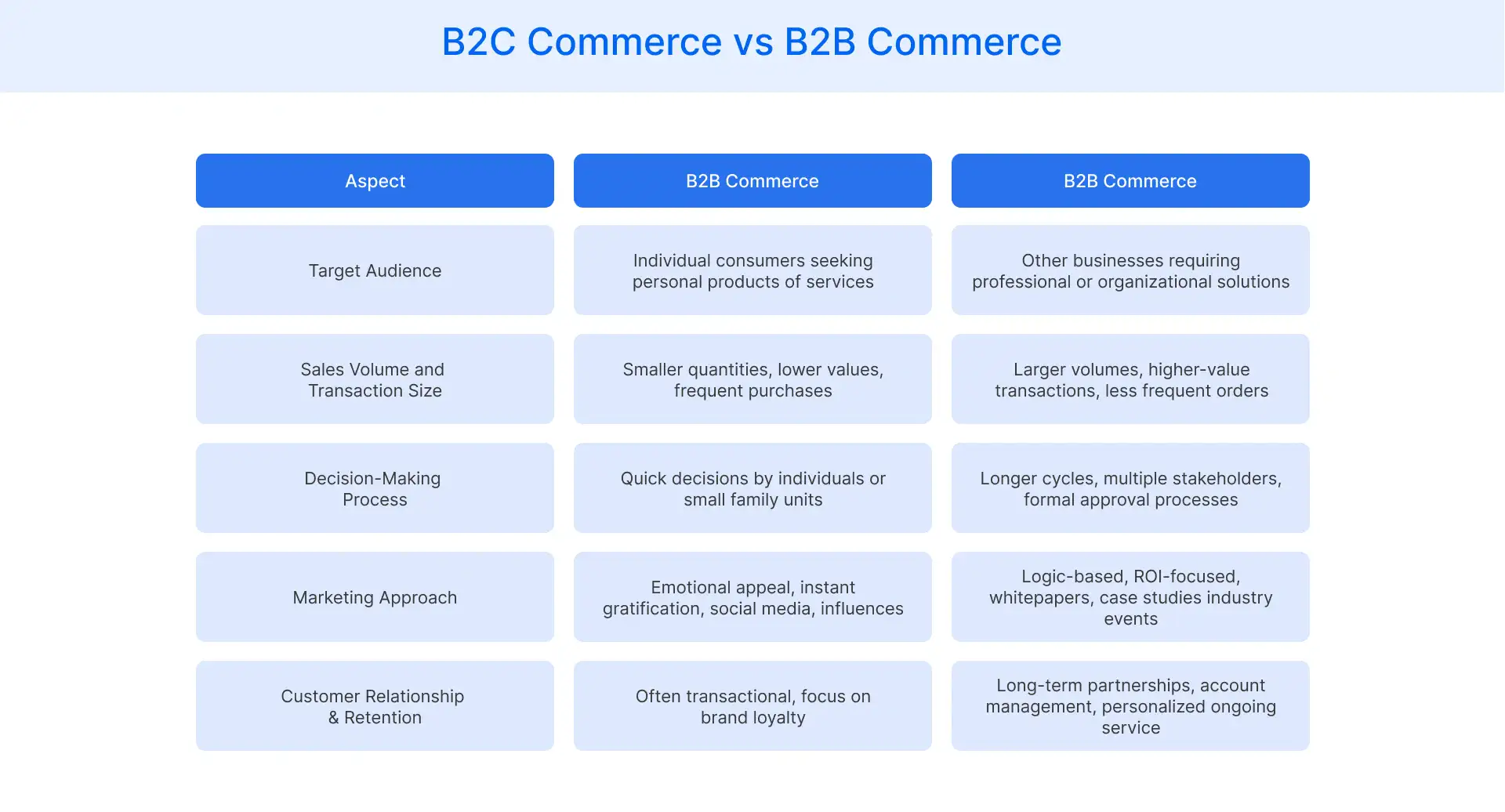
B2C vs B2B Commerce: Key Differences
B2C commerce and B2B commerce differ significantly in how transactions are structured and managed, from target audience to customer retention strategies.
- Target Audience: B2C commerce targets individual consumers seeking products for personal use, while B2B commerce serves businesses purchasing goods or services for operational needs.
- Sales Volume and Transaction Size: B2C transactions involve smaller, individual purchases, while B2B sales often feature bulk orders with higher transaction values.
- Decision-Making Process: B2C buyers make quick, personal decisions, while B2B purchases typically involve multiple stakeholders and longer approval cycles.
- Marketing Approach: B2C marketing focuses on emotional appeals and product benefits, while B2B strategies highlight value, efficiency, and ROI.
- Customer Relationships & Retention: B2C relationships are often transactional, with loyalty driven by satisfaction, while B2B relationships emphasize long-term partnerships and tailored support.
Key Features of B2C Commerce
B2C commerce is characterized by the following features that shape its ecosystem and drive its success:
- Direct-to-consumer sales: Consumers can purchase products or services directly from businesses without intermediaries. This model eliminates middlemen, potentially reducing costs and streamlining the buying process for consumers.
- Personalization and targeted marketing: B2C commerce leverages data analytics to tailor the shopping experience. Consumers receive personalized product recommendations, customized offers, and targeted advertisements based on their browsing history, purchase behavior, and preferences.
- Fast and convenient purchasing: B2C platforms prioritize user-friendly interfaces and streamlined checkout processes. Transactions can be completed quickly, often with just a few clicks, enhancing the overall shopping experience on the Internet.
- Mobile and omnichannel commerce: Shopping can be done seamlessly across various devices and platforms. Whether using a smartphone, tablet, or computer, B2C commerce ensures a consistent and integrated experience across all channels.
-
Customer experience focus: B2C businesses prioritize customer satisfaction at every touchpoint. From intuitive website design to responsive customer support, the goal is to create a positive and memorable shopping journey for the consumer by using platforms like Salesforce Commerce Cloud.
-
Real-time inventory and pricing: Consumers benefit from up-to-date product availability and dynamic pricing. B2C commerce systems often update inventory and adjust prices in real-time, ensuring transparency and helping customers make informed decisions.
Types of B2C Commerce Models
Here are the primary types of B2C commerce models:
- Direct Sellers: Direct sellers manufacture and sell products directly to consumers without intermediaries. This model allows for greater control over the customer experience and brand messaging. Examples include Apple’s online store and Dell’s custom-built computers.
- Online Intermediaries: These platforms connect buyers and sellers without owning the products themselves. They facilitate transactions and often provide additional services like secure payments and dispute resolution. eBay is a prominent example of online intermediaries in B2C commerce.
- Advertising-Based Model: This model offers free content or services to consumers while generating revenue through targeted advertising. Social media platforms like Facebook and content providers such as YouTube primarily use this approach, leveraging user data to deliver personalized ads.
- Community-Based Model: Community-based B2C commerce builds on shared interests or demographics to create engaged customer bases. These platforms often combine e-commerce with social features, fostering user-generated content and peer recommendations. Etsy, catering to handmade and vintage item enthusiasts, exemplifies this model.
- Subscription-Based Model: Subscription services provide ongoing access to products or content for a recurring fee. This model ensures steady revenue streams and fosters long-term customer relationships. Netflix for streaming entertainment and Blue Apron for meal kits are successful examples of subscription-based B2C commerce.
Advantages of B2C Commerce
B2C commerce offers several compelling benefits for businesses and consumers alike:
- Wider Market Reach: Digital platforms enable you to tap into a global audience, transcending geographical boundaries. Your products can reach customers in different time zones and countries, significantly expanding your potential customer base.
- Lower Operational Costs: Online stores eliminate the need for physical storefronts, reducing overhead expenses. You can allocate resources more efficiently, focusing on product quality and customer service rather than maintaining brick-and-mortar locations.
- Faster Purchasing Process: Customers can browse, compare, and buy products instantly, 24/7. This convenience accelerates the sales cycle and improves customer satisfaction, potentially leading to increased sales and repeat business.
- Personalized Shopping Experience: AI-driven recommendations enhance customer engagement by offering tailored product suggestions. You can leverage customer data to create personalized marketing campaigns and improve overall user experience.
- Real-time Inventory Management: B2C commerce platforms allow you to update stock levels instantly, preventing overselling and improving inventory turnover rates. This real-time visibility helps in making informed restocking decisions.

Challenges in B2C Commerce
Despite its advantages, B2C commerce also presents several challenges:
- High Competition: The low barriers to entry in online retail lead to a saturated market. You must continuously innovate and differentiate your offerings to stand out among numerous competitors vying for customer attention.
- Customer Retention Challenges: While acquiring customers online can be easier, retaining them is often more difficult. To encourage repeat purchases, you need to implement robust loyalty programs and consistently deliver exceptional experiences.
- Logistics and Supply Chain Manamenget: Ensuring seamless order fulfillment and timely delivery can be complex, especially when operating across multiple regions. You must optimize your supply chain to meet customer expectations for fast and reliable shipping.
- Regulatory Compliance: Adhering to digital commerce regulations and data privacy laws is crucial. You must stay updated on evolving legal requirements across different jurisdictions to protect your business and customer data.
- Cybersecurity Threats: As B2C commerce relies heavily on digital transactions, protecting against cyber attacks and data breaches is paramount. You need to invest in robust security measures to safeguard sensitive customer information and maintain trust.
Conclusion
In today's digital economy, B2C commerce is pivotal, enabling businesses to connect directly with consumers and expand their market presence. To remain competitive, it's essential to adopt emerging technologies and implement consumer-centric strategies. At Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC), we offer solutions designed to enhance your B2C operations.
Our Digital Commerce Solution provides a modular and scalable e-commerce platform, allowing you to create personalized shopping experiences and manage diverse customer journeys seamlessly. Additionally, our Retail Media Platform leverages advanced AI/ML algorithms to deliver personalized advertisements, increasing engagement and driving higher return on ad spend.
By integrating our innovative solutions, you can effectively navigate the evolving B2C landscape and achieve sustainable growth.
FAQ
The skills needed for B2C sales include strong interpersonal communication, empathy, and the ability to close transactions quickly in a retail environment. Successful sales professionals in this space must also possess deep product knowledge and the ability to build rapport with diverse personalities almost instantly.
The role storytelling plays in B2C marketing is to build an emotional bond between the brand and the individual shopper. Effective narratives transform a simple product into a necessary lifestyle solution. FCC helps brands amplify these narratives by providing the retail media tools necessary to deliver the right story to the right audience at the perfect moment in their journey.
B2C is a popular business model because it offers direct access to a massive global audience and results in shorter sales cycles. This direct relationship allows for immediate market feedback and total brand control. Entrepreneurs can capitalize on this popularity by using scalable technology to reach millions of consumers across multiple digital channels with ease.
The 5 types of business-to-consumer models consist of direct sellers, online intermediaries, advertising-based models, community-based models, and fee-based models. Direct sellers include manufacturers selling through their own sites, while intermediaries like Expedia bring buyers and sellers together; advertising models rely on high traffic to sell ad space, and fee-based models like Netflix charge for content access. These structures allow brands to reach users through various methods, from manufacturing products to hosting social communities.
B2C companies handle customer data privacy by implementing robust encryption protocols and secure payment gateways that protect sensitive information. These businesses strictly follow global regulations like GDPR and CCPA to maintain user trust. By using Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC), retailers gain access to secure infrastructures that prioritize confidentiality and data integrity.
B2C retail refers to the direct sale of physical goods to individual consumers for personal use. Common instances include buying groceries at a supermarket or purchasing sneakers from an online store. Modern retailers use FCC to manage these inventory levels and provide a personalized experience across all shopping platforms.
B2C makes money by selling products or services to individual consumers at a retail price that exceeds the cost of goods and operations. Revenue also flows from subscriptions, service fees, or targeted advertising. By leveraging the financial insights, companies can optimize their pricing to ensure consistent growth in a competitive consumer market.

