Table of Contents
- What is Dead Stock?
- Why is Dead Stock a Problem?
- How to Identify Dead Stock
- Causes of Dead Stock
- Strategies to Manage Dead Stock
- Tools to Help Manage Dead Stock
- Conclusion
What is Dead Stock?
Dead stock, also called obsolete inventory, consists of products that remain unsold over a prolonged period and are unlikely to generate revenue. Such inventory can result from over-purchasing, inaccurate demand forecasting, or shifts in consumer preferences. Failure to analyze historical sales data combined with poor inventory management are also among the common causes behind an increase in dead stock costs.
Unlike slow-moving items, dead stock typically offers no immediate sales potential and often requires businesses to take remedial actions such as discounting or liquidation. Effectively managing dead stock is essential to freeing up resources and maintaining healthy cash flow.
Why is Dead Stock a Problem?
Dead stock creates significant challenges for businesses, impacting financial health, operational efficiency, and overall profitability. Here are the key issues this problem leads to:
- Increased Storage Costs: Dead stock occupies valuable space on warehouse shelves, leading to higher storage costs. This includes expenses for rent, utilities, and labor required to manage unsellable inventory.
- Reduced Cash Flow: Unsold inventory ties up capital that could be reinvested in profitable ventures. This limits your ability to purchase high-demand products or fund essential business operations.
- Operational Inefficiencies: Managing dead stock diverts time and resources from productive activities. Tasks like inventory audits, stock movement, and eventual disposal increase operational burdens without generating revenue.
- Product Depreciation and Obsolescence: Items lose value over time due to trends, technological advancements, or expiration. This further reduces the chances of recovering costs through sales or liquidation.
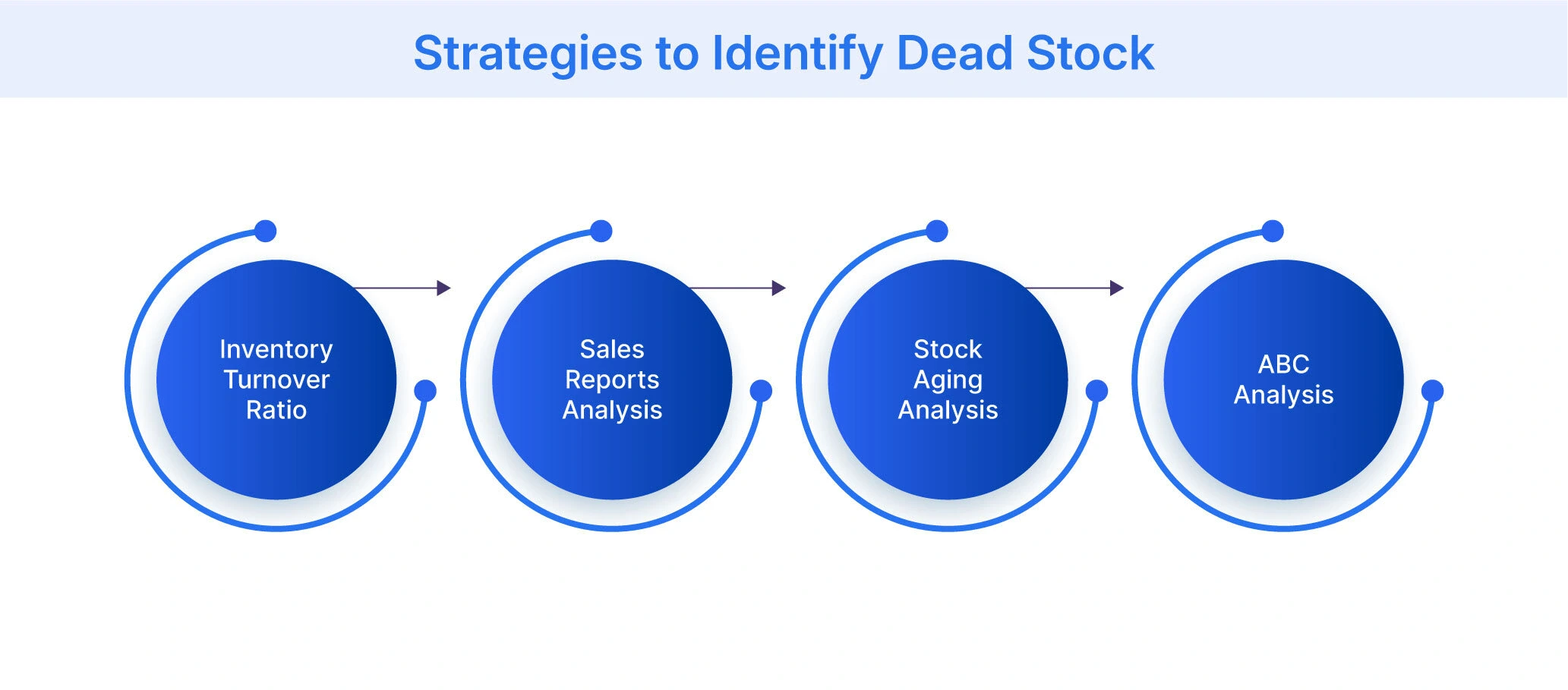
How to Identify Dead Stock?
Here are four effective methods for identifying dead stock and minimizing cost of dead stock:
- Inventory Turnover Ratio: Businesses calculate this ratio by dividing the cost of goods sold by the average inventory value. A low ratio for specific items, compared to the industry standard, may indicate dead stock. For instance, if the average turnover for electronics is 5, but hair dryers have a ratio of 1, they might be considered dead stock.
- Sales Reports Analysis: Companies should regularly review their sales data to identify products with consistently low or no sales over an extended period. Setting a threshold, such as items not sold in the last 6-12 months, can help flag potential dead stock. This method could reveal seasonal items like winter coats that are still in stock during summer.
- Stock Aging Analysis: Implementing an aging report that categorizes inventory based on how long it has been in the valuable warehouse space is crucial. Items sitting for longer than the typical sales cycle are likely dead stock. For example, if fast-fashion retailers typically sell items within 3 months, anything older could be problematic.
- ABC Analysis: Businesses categorize their inventory into A (fast-moving), B (moderate-moving), and C (slow-moving) items. Products consistently falling into the C category across multiple periods are strong candidates for dead stock. This method helps identify underperforming product lines or variations.
Causes of Dead Stock
Understanding the different reasons behind surplus inventory turning into dead stock is crucial for implementing effective prevention strategies:
Over-Purchasing Inventory
Retailers often overestimate customer demand, leading to excess stock. This can result from bulk-buying discounts or minimum order quantities imposed by suppliers. For example, a small boutique might order too many trendy handbags, anticipating future demand that doesn't materialize.
Poor Demand Forecasting
Inaccurate sales predictions can leave businesses with unsold inventory. Failing to account for market trends, economic shifts, or changing consumer preferences can increase the risk of dead stock. For example, an electronics store might overstock on a particular smartphone model, unaware of a competitor's upcoming release.
Seasonal Product Obsolescence
Products tied to specific seasons or events quickly become outdated. Holiday decorations, summer fashion, or themed merchandise can become dead stock inventory if not sold within their intended timeframe. For example, unsold holiday decorations after Christmas often turn into dead stock unless cleared through discounts or promotions.
Lack of Marketing Efforts
Insufficient promotion can result in products languishing on shelves. Without effective marketing strategies, even high-quality items may go unnoticed by potential customers. For example, a new line of organic skincare products might become dead stock if not properly advertised or prominently displayed in-store.
Supply Chain Issues
Delays or disruptions in the supply chain can lead to excess inventory before it reaches customers. This is particularly problematic for perishable goods or fast-moving tech products. For example, transportation delays can cause late delivery of summer apparel during the fall, resulting in unsellable stock due to missed seasonal demand.

Strategies to Manage Dead Stock
Here are some actionable inventory management strategies retailers can implement for maintaining a healthy inventory and improving cash flow:
- Implement Strategic Discounting: Offer tiered discounts based on inventory age. Start with modest markdowns and gradually increase them to attract price-sensitive customers without immediately resorting to extreme measures.
- Create Product Bundles: Pair slow-moving items with popular products to increase their appeal. This strategy can help move dead stock while maintaining reasonable profit margins on the bundle as a whole.
- Utilize Alternative Sales Channels: Explore online marketplaces, pop-up shops, or consignment stores to reach new customer segments. These channels can provide fresh exposure for your stagnant inventory.
- Supplier Agreements: Negotiate flexible return or exchange policies with suppliers. Such arrangements mitigate risks by allowing return of unsold inventory, minimizing dead stock accumulation and preserving financial stability.
- Donate to Charity: Consider donating unsold items to local charities or non-profit organizations. This approach can generate goodwill, potentially lead to tax benefits, and free up valuable storage space.
Tools to Help Manage Dead Stock
Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC) provides a highly effective inventory management software designed to help businesses track stock movement, identify slow-moving products, and optimize replenishment cycles. Our tools are powered by machine learning to ensure efficiency and accuracy.
- One of our key solutions is the Warehouse Management System (WMS), which provides real-time visibility into stock levels across multiple locations. It ensures seamless inventory movement monitoring and helps identify potential dead stock early.
- FCC's advanced analytics tools improve inventory management system at the SKU and channel levels, providing accurate forecasting capabilities. This feature helps businesses anticipate demand fluctuations and adjust inventory levels to lower the risk of overstocking and creating dead stock.
- Our Price Optimization Manager enables businesses to optimize pricing strategies by analyzing competitor data and customer behavior. This tool helps adjust prices dynamically, ensuring that slow-moving products are priced competitively to encourage sales.
By leveraging these solutions from FCC, retailers can create personalized customer experiences while driving greater operational efficiencies and profitability.
Conclusion
Effectively managing dead inventory is essential for maintaining profitability and operational efficiency. By actively monitoring inventory levels, businesses can identify slow-moving products early and take corrective actions. Implementing strategies such as accurate demand forecasting, dynamic pricing, and regular stock audits reduces the risk of accumulating unsold inventory. Proactive inventory management practices ensure businesses remain agile and competitive in a dynamic market.
FAQ
Inventory is typically considered dead stock if it remains unsold for 12 months or more. However, this timeline may vary depending on the product type and industry trends. Regular stock audits can help identify such inventory early.
Yes, unsold stock can be converted into active inventory through strategies like repurposing, rebranding, or bundling with trending products. For instance, unsold seasonal items can be repurposed for upcoming promotions or paired with complementary products to boost sales.
E-commerce businesses can manage obsolete stock by offering discounts, bundling slow-moving items with popular products, or utilizing alternative sales channels like online marketplaces. For example, bundling unsold accessories with high-demand items can attract buyers and clear inventory efficiently.

