Table of Contents
- What is loss leader pricing?
- Example of loss leader pricing
- The rationale behind loss leader pricing
- Types of loss leader pricing strategies
- How to use loss leader pricing in your business?
- Benefits and challenges of using loss leader pricing
- Conclusion
What is Loss Leader Pricing?
A loss leader pricing strategy involves setting prices below cost to boost sales of more profitable items. This approach aims to attract customers from competitors by offering certain goods at a loss. Unlike predatory pricing, which seeks to eliminate competition, loss leader pricing focuses on driving sales of higher-margin products.
By sacrificing profit on specific items, retailers can increase overall revenue through the sale of complementary and profitable goods. This pricing strategy effectively drives additional purchases, ultimately benefiting the business's bottom line.
Example of loss leader pricing
Walmart, a retail giant, often employs a loss leader pricing strategy to attract customers. For instance, during Black Friday sales, Walmart offers popular electronics like televisions and gaming consoles at prices significantly below cost. This type of pricing strategy aims to draw large crowds into their stores.
While Walmart incurs losses on these discounted items, the increased foot traffic leads to higher sales of other products with better profit margins, such as accessories, groceries, and household items. This approach not only boosts overall sales but also enhances customer loyalty and market presence.
However, retailers must carefully manage such strategies to avoid potential financial pitfalls.
The rationale behind loss leader pricing
The loss leader marketing strategy is a popular retail pricing method. It involves selling certain products below cost, which can actually benefit a retail business when implemented effectively.
The underlying principle of this strategy is that offering products at a loss can attract more customers, who may then purchase other, higher-margin items, ultimately increasing overall sales. Many retailers employ a 'bait and switch' tactic. They use low-priced products to attract customers to their platforms, with the expectation that they will also purchase other, more profitable items.
A common example of this strategy is the use of 'introductory' pricing for products and services. Many online retailers offer significant discounts on seasonal items at the beginning of the season to encourage customers to try their products.
Types of loss leader pricing strategies

Pricing strategies are rarely a one-size-fits-all approach in the world of retail sales. This is why different retailers implement it in a range of ways:
Introductory Pricing
This strategy offers customers a low initial price for a product, followed by a higher price later. It encourages new customers to try the product without a significant upfront investment. For example, a streaming service might offer the first three months at half price before charging the full subscription rate.
Store Placement
Products like bread and fresh produce are often placed at the back of the store, so customers pass by other higher-margin items. This tactic maximizes exposure to additional products, increasing the likelihood of impulse purchases while maintaining overall profitability.
Inventory Management
Businesses use this strategy to clear out outdated or seasonal stock. For example, a clothing retailer might sell winter coats at a steep discount in early spring. This helps to free up space for new collections and avoid holding unsold inventory.
Free Samples
Offering free samples encourages customers to try new products and builds a sense of reciprocity. For example, a coffee shop might give away samples of a new beverage, prompting customers to purchase a full cup later. This approach often increases sales by creating brand loyalty.
How to use loss leader pricing in your business?
Implementing a loss leader strategy effectively requires careful planning and execution. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you get started:
- Select the Right Product or Service: Choose products that are desirable and enticing enough to attract customers but not so crucial that selling them at a loss will harm your overall profitability.
- Set Clear Objectives: Define your goals, whether it's increasing foot traffic, boosting online sales, or clearing out inventory. With clear objectives, you will be in a better position to measure success and make necessary adjustments.
- Determine the Scope and Scale: Decide how many units you can offer at a loss and for how long. This depends on your inventory levels, financial resilience, and objectives. Limiting availability can create urgency while protecting your margins.
- Price Strategically: Set a price low enough to attract customers but not so low that it devalues your brand or results in unsustainable losses. The key is to find a balance that makes your product appealing without harming your brand's reputation.
- Promote Effectively: Utilize all available marketing channels, including online ads, email marketing, social media, and in-store signage. Highlight the value of your loss leader and tease complementary products or services.
- Monitor and Adjust: Track metrics like foot traffic, sales volume, and customer acquisition costs. You should be prepared to update your approach as per the data to ensure the strategy's effectiveness.
- Follow-Up and Engage: After customers take advantage of your loss leader offer, nurture them with follow-up marketing to encourage repeat purchases. Use personalized email marketing, special offers, or loyalty programs to keep them coming back.
Pros and cons of using loss leader pricing
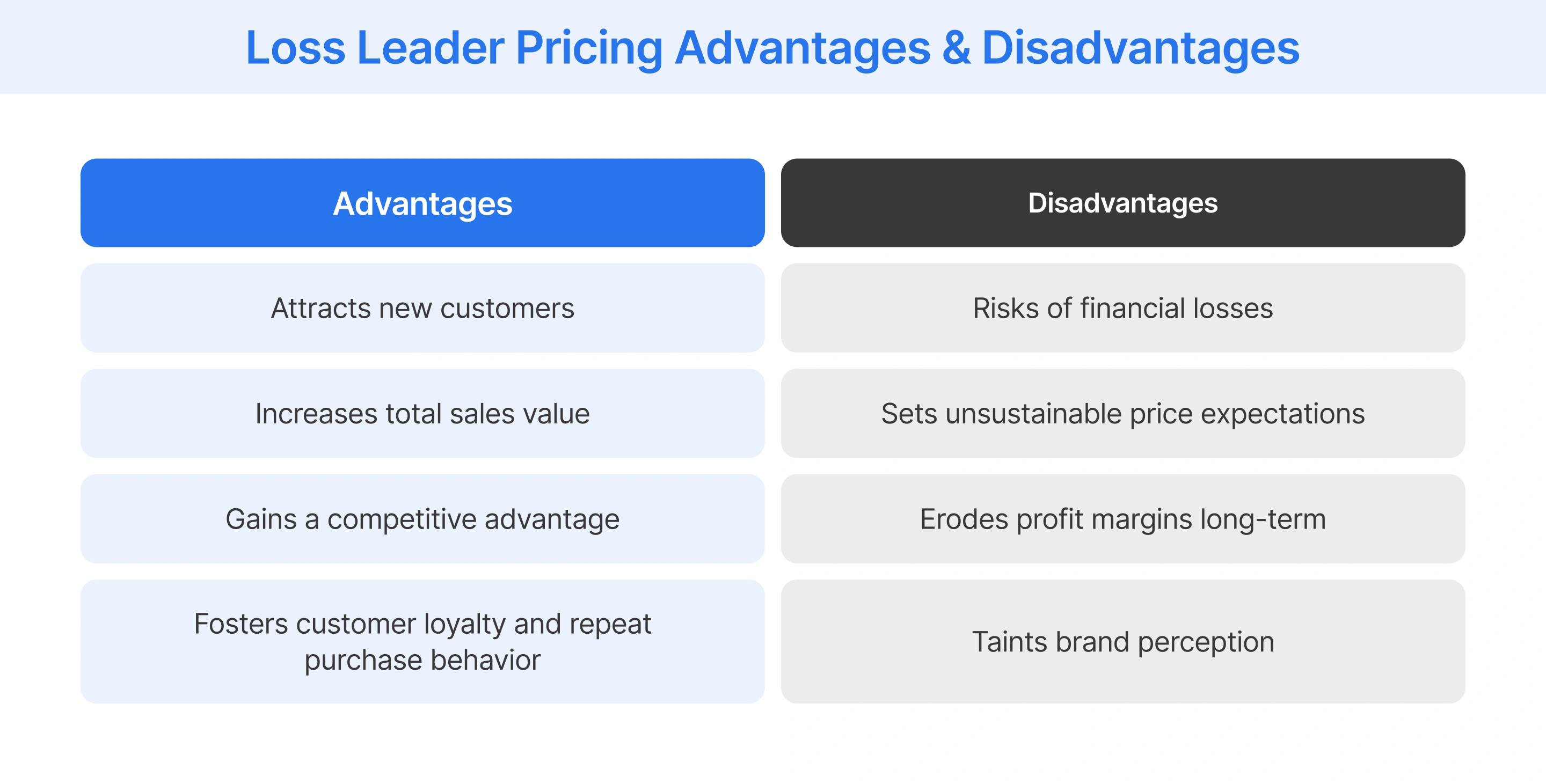
Retailers can leverage loss leader pricing as a useful strategy to drive sales and market penetration. However, careful consideration is required to avoid adverse financial outcomes and potential customer dissatisfaction.
Benefits of loss leader pricing
- Market Expansion: By employing a loss leader strategy, retailers can attract consumers who might not have been aware of their offerings. This can help with the expansion of the customer base and improvement in brand recognition.
- Sales Growth: Loss leaders can serve as a gateway to additional sales of higher-margin products or services. Customers attracted by the initial discount may be more likely to purchase other items at full price.
- Market Dominanc: This strategy is particularly effective for retailers entering new markets or launching new products. Loss leader pricing can help to gain market share and establish a presence quickly.
- Customer Retention: A positive experience with a loss leader can foster customer loyalty and encourage repeat business. According to a recent Salesforce report, 88% of customers are more likely to make repeat purchases following a positive customer service experience.
Challenges of loss leader pricing
- Revenue Leakage: Excessive discounts without corresponding increases in higher-margin sales can lead to financial losses. To mitigate this risk, retail businesses should implement strategies such as limiting the quantity or duration of the offer.
- Customer Perception: Overreliance on loss leader pricing can create unrealistic customer expectations regarding prices. To avoid this, retailers should clearly communicate the temporary nature of discounts and focus on providing value beyond price.
- Margin Erosion If customers do not convert to regular pricing or continuously seek out discounts, the initial loss on the loss leader can negatively impact the company's overall profitability.
- Brand Image: Excessive use of loss leader pricing can damage a brand's reputation by creating the perception of a low-quality or discount-oriented business. To avoid this, retail businesses should consider offering loss leaders only on special occasions or as rewards for loyal customers.
Conclusion
Loss leader pricing is a strategic retail pricing approach where businesses sell certain products at a loss to attract customers and boost sales of more profitable items. When implemented effectively, it can increase foot traffic, enhance customer loyalty, and drive overall revenue. However, careful planning, strategic pricing, and continuous monitoring are essential to avoid potential financial pitfalls and ensure the strategy benefits the business's bottom line.
FAQ
A loss leader in pricing is a strategy where a product is sold below its market cost to stimulate the sale of other, more profitable goods. This tactic aims to attract customers into a store or onto a digital platform with the expectation that they will complete their purchase with additional items. Retailers often use this as a customer acquisition tool, frequently leveraging the strategic placement and data insights provided by FCC to ensure the increased basket size offsets the initial loss on the leader item.
Loss leader pricing does not violate pricing laws in most free-market economies unless it is used specifically as a predatory tactic to eliminate competition. While the practice is generally legal in the United States at the federal level, several individual states have specific statutes that restrict or prohibit selling below cost. Businesses often rely on the transparent reporting and compliance features within the FCC ecosystem to document that their pricing strategies are legitimate promotional efforts rather than prohibited anti-competitive behaviors.
Loss leader pricing is widely used in the retail sector, where grocery stores and supermarkets offer essential items like milk and bread at low prices to drive sales of more profitable goods. Similarly, an ecommerce business can use this strategy to drive traffic to their platforms by offering significant discounts on popular items. Likewise, business owners in the hospitality and entertainment sectors, such as restaurants and cinemas, use loss leader pricing to attract customers with discounted meals or tickets, encouraging additional spending on beverages and snacks.
Loss leader pricing is beneficial because it attracts customers and increases foot traffic, leading to higher sales of more profitable items. This aggressive pricing strategy helps retail businesses clear out old inventory, introduce new products, and build customer loyalty. Offering compelling deals can help retailers stand out from their competitors and encourage customers to purchase immediately. This strategy can enhance brand visibility and drive long-term revenue growth through repeat purchases and cross-selling opportunities.
Examples of loss leader pricing can be found across various segments. Electronics retailers may sell popular gadgets at a loss to drive sales of accessories and warranties. Similarly, pharmacies might offer discounted over-the-counter medications to encourage purchases of higher-margin prescription drugs. Likewise, bookstores sometimes sell bestsellers at a loss to increase foot traffic and boost sales of other books and merchandise.
The best type of loss leader pricing strategy for your business depends on your specific goals and industry. Introductory pricing is ideal for launching new products and attracting first-time buyers. Store placement works well for grocery stores, as essential items are placed at the back to increase exposure to other products. Inventory management is effective for clearing out old retail stock. Free samples are great for food and beverage businesses to encourage trial and repeat purchases. However, you must choose a strategy that aligns with your objectives and customer behavior.

