Table of Contents
- What is Decoy Pricing?
- How does Decoy Pricing work?
- Example of Decoy Pricing
- What are the benefits of Decoy Pricing?
- Decoy Pricing use cases: Where is it used
- How to implement Decoy Pricing strategy?
- What are the disadvantages of Decoy Pricing?
- What is the impact of Decoy Pricing on customers and business revenue?
- Conclusion
Decoy pricing is a strategy where an additional product option is introduced with the sole purpose of steering buyers toward the target. The decoy product is priced close to the target product but offers fewer features or lower value. The presence of the decoy creates the attraction effect, nudging customers toward the option that appears to provide better value.
This business strategy leverages consumer psychology and cognitive bias. By presenting different prices across price tiers, businesses highlight the product value of the target while making alternatives seem like a good deal only in comparison.
Let’s have a look at the key features of decoy pricing:
- Encourages customers to select the higher-value option over a cheaper or less beneficial choice.
- Works by highlighting differences between two or more product tiers.
- Increases average order value without altering core product offerings.
- Simplifies customer decision-making by presenting a clear “best” option.
- Commonly applied in subscription services, retail bundles, and online product comparisons.
How Does Decoy Pricing Work?
The effectiveness of the decoy pricing method lies in the idea of relative value rather than absolute worth. Customers often lack a precise sense of a product’s intrinsic value, so they compare available pricing options instead. Introducing a decoy creates a new reference point that is intentionally less appealing than the target choice, making the preferred product appear valuable in comparison.
The decoy is structured to be “asymmetrically dominated.” It may be priced slightly below the target but offer far fewer features or positioned at a similar price while clearly inferior in quality. This deliberate imbalance highlights the target product as the most rational and beneficial option.
By shaping the decision environment in this way, businesses can subtly steer customers toward higher-margin products or services. The decoy effect simplifies choice, provides a mental shortcut, and makes the added value of the target product more visible and convincing.

Examples of Decoy Pricing
Here are three examples that illustrate how this powerful pricing strategy is commonly applied in different sectors.
- The Economist Subscription: The print-only subscription at $125 served as a classic decoy. Since the web-and-print bundle was offered at the exact same price, the decoy was clearly an inferior choice. This comparison framed the bundle as an incredible deal, effectively making the web access feel free and successfully nudging customers away from the cheaper $59 option.
- Cinema Popcorn Sizes: In this scenario, the medium popcorn is the decoy, priced disproportionately high at $6.50. Customers see a large price jump from small to medium but a very small one from medium to large. This pricing structure makes the large size at $7 appear to be the most logical and high-value choice for just 50 cents more.
- Software Service Tiers: Here, a "Pro" plan acts as the decoy by offering only minor feature additions over the "Basic" plan for a considerable price increase. The "Premium" plan, however, provides a full suite of features for only a small amount more than the "Pro" plan, making it the clear high-value option and encouraging an easy upsell.
What Are the Benefits of Decoy Pricing?
Implementing a decoy pricing strategy can yield significant advantages for retail and e-commerce businesses by subtly influencing consumer behavior.
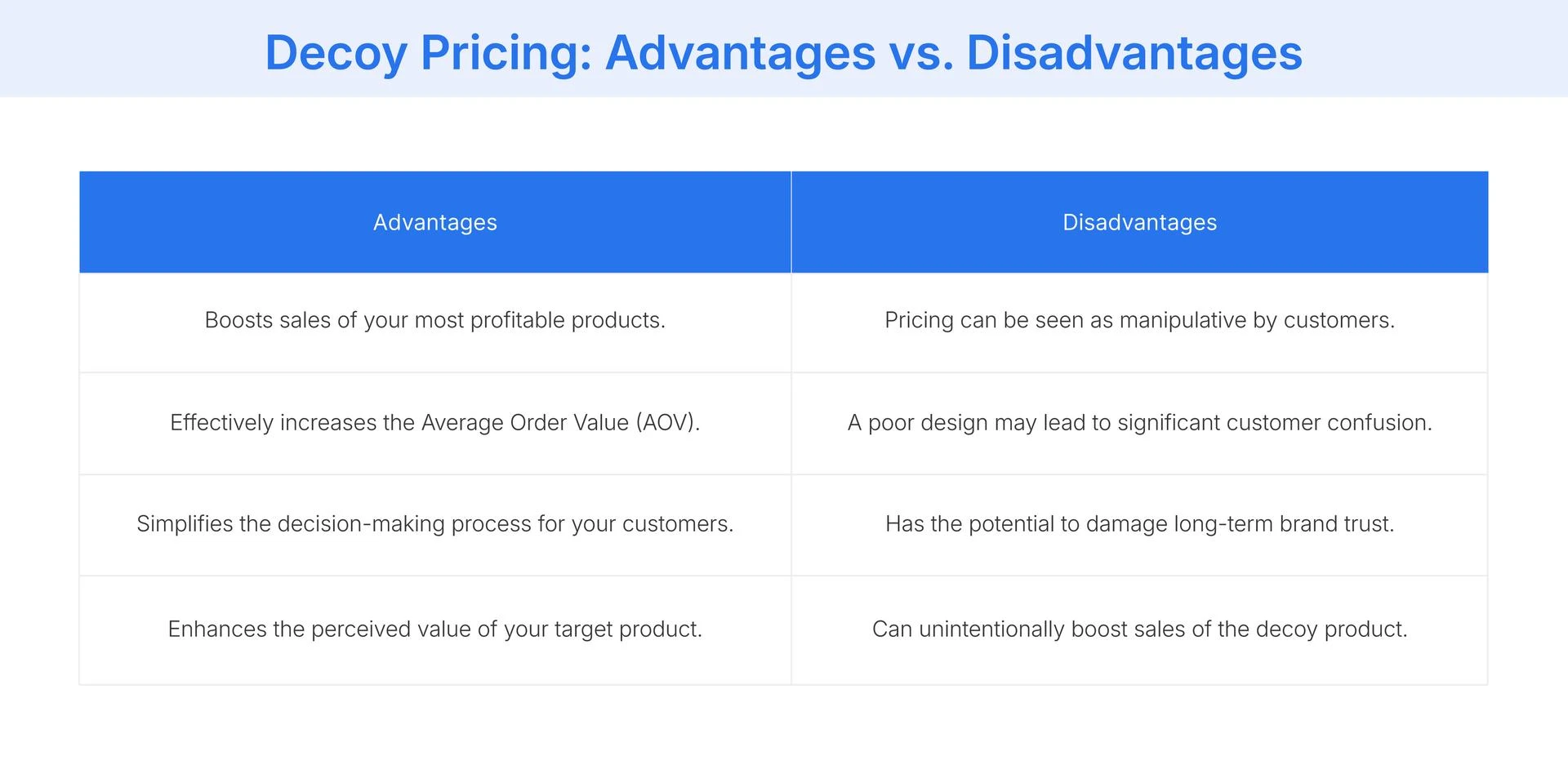
- Increased Sales of Target Products: It effectively nudges customers toward purchasing the profitable or feature-rich option you want to promote, directly boosting sales volume for specific items.
- Higher Average Order Value (AOV): By encouraging customers to upgrade from the cheapest option, this strategy successfully increases the average amount spent per transaction across your customer base.
- Simplified Customer Decisions: It reduces choice paralysis by providing a clear "winner" among the options, which improves the customer experience and can accelerate the path to purchase.
- Enhanced Perception of Value: The decoy makes the target product appear as a high-value bargain, which can improve customer satisfaction and their overall perception of your brand's pricing.
- Improved Product Mix Sales: It allows businesses to strategically manage inventory and sales distribution by promoting specific products without resorting to traditional discounts or promotions.
Decoy Pricing Use Cases: Where Is It Used?
This strategy is versatile and can be found across various industries to guide customer choices and maximize revenue streams effectively.
- Subscription Services: SaaS companies and media publishers frequently use tiered pricing models with a decoy option to upsell customers to annual plans or premium tiers with advanced features and support.
- Food and Beverage: Restaurants and cafes use it on menus for items like drinks, meals, and desserts, making the larger or combo options seem like a better financial choice for a small price increase.
- E-commerce Product Variants: Online stores apply this tactic to products with multiple versions (e.g., storage capacity for electronics), where a mid-tier option makes the top-tier model look superior.
- Travel and Hospitality: Airlines and hotels use decoys in ticket classes or room packages, where a slightly expensive "premium economy" or "deluxe room" offers disproportionately higher value than a "standard" option.
How to Implement a Decoy Pricing Strategy?
A successful implementation of decoy pricing requires careful analysis and strategic planning rather than simply adding a random third option to your lineup. Here are the steps you must follow for a seamless implementation:
Conduct Product and Customer Analysis
Begin by analyzing sales data to identify a high-margin or high-value product you wish to promote (the target). Use customer analytics and segmentation data to understand purchasing patterns. Determine which customer segments are most likely to be influenced by value-based comparisons and which products are frequently compared during the buying journey.
Architect the Three-Tier Structure
Design the three options: the cheapest option, the target option, and the decoy. The target must asymmetrically dominate the decoy. For example, if your target product is $100, the decoy could be priced at $95 but offer significantly fewer features, making the target's value proposition clear for just $5 more.
Design the User Interface (UI)
The visual presentation is critical. In an e-commerce setting, use UI design to highlight the target option. This can be achieved through visual cues, such as a "Most Popular" banner, a larger button, a different color, or by pre-selecting it. The layout should guide the customer's eye to compare the decoy and the target easily.
Execute Controlled A/B Tests
Before a full rollout, validate the strategy with A/B testing. Use platforms like Google Optimize or VWO to present the decoy pricing structure to a segment of your audience while the control group sees the original two-option pricing. Measure metrics like conversion rate, AOV, and revenue per visitor to confirm its effectiveness.
Monitor Performance and Iterate
After implementation, continuously monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) through your analytics dashboard. Flipkart Commerce Cloud enables this through tools like Pricing Manager for real-time competitor tracking and demand analysis, and Pricing Optimizer for forecasting revenue across scenarios. These tools can help you refine decoy and target options based on performance and evolving market conditions.
What Are the Disadvantages of Decoy Pricing?
While effective, this strategy carries potential risks and downsides that retailers must consider before and during its implementation.
- Risk of Brand Damage: If customers perceive the pricing as manipulative or deceptive, it can erode trust and negatively impact your brand's reputation for transparency and fairness.
- Potential for Customer Confusion: A poorly designed decoy that doesn't create a clear value distinction can confuse customers, leading to choice paralysis and potentially abandoned carts.
- Cannibalization of Sales: If the decoy is accidentally too appealing or the target is not compelling enough, you might inadvertently sell more of the decoy, defeating the strategy's purpose.
- Complexity in Management: Maintaining a decoy strategy requires ongoing analysis and testing, adding complexity to your pricing management, especially across a large product catalog.
What is the Impact of Decoy Pricing on Customers and Business Revenue?
For customers, the primary impact of decoy pricing is a simplification of their decision-making process. It provides a clear cognitive shortcut, making them feel confident and justified in choosing the target product, which they perceive as the best value. This can lead to higher satisfaction with the purchase, as the framework has helped them feel like they made a smart and rational choice.
From a business perspective, the impact on revenue can be substantial. The strategy is designed to steer customers toward higher-priced, higher-margin items, which directly increases the average order value. By upselling customers from the lowest-priced option, businesses can see a significant lift in overall revenue without altering the products themselves or investing in large-scale marketing campaigns.
However, this positive financial impact is contingent on successful execution. If customers see through the strategy and feel manipulated, it can lead to short-term gains but long-term brand erosion. Therefore, the long-term impact on revenue is tied to maintaining customer trust while subtly guiding their purchasing behavior.
Conclusion
Decoy pricing is an advanced psychological tool that, when implemented ethically and strategically, can significantly influence consumer behavior. By introducing a carefully crafted third option, retailers can frame their product offerings to make a target item or an appealing one, leading to increased sales and higher revenue. Success depends on data analysis, thoughtful execution, and continuous monitoring.
FAQ
Decoy pricing is considered ethical when it helps customers make clearer decisions about value. However, it can become unethical if it is used to intentionally mislead or deceive consumers into making choices that are not in their best interest.
Yes, numerous studies and real-world examples show it is highly effective. It leverages cognitive biases to make a specific product seem attractive, often leading to increased sales for that item and a higher average transaction value for the business.
Undercutting prices is generally legal and a common competitive practice. It becomes illegal only when it is part of "predatory pricing"—the practice of setting prices extremely low to eliminate competitors and monopolize the market, which violates antitrust laws.
Unlike charm pricing (e.g., $9.99) which focuses on the left-digit effect, decoy pricing is a comparative strategy. Its effectiveness relies on the context created by other available options, not on the price number of a single product itself.
Absolutely. If your decoy pricing is too obvious or seems overtly manipulative, customers may lose trust in your brand. Transparency is key, and the value proposition of the target option must be genuine to avoid backlash and protect your reputation.

