Table of Contents
- What is a Fulfillment Center?
- Key Functions of a Fulfillment Center
- Types of Fulfillment Centers
- Fulfillment Center vs. Traditional Warehouse
- How to Choose the Right Fulfillment Center?
- Benefits of Using a Fulfillment Center
- Challenges in Fulfillment Center Operations
- Conclusion
What is a Fulfillment Center?
A fulfillment center is a specialized facility designed to efficiently process and ship orders for e-commerce and retail businesses. Unlike traditional warehouses that primarily focus on long-term storage, fulfillment centers are dynamic hubs optimized for rapid order processing and distribution.
These centers serve as crucial links in the supply chain, bridging the gap between manufacturers, retailers, and end consumers. They handle various tasks, including receiving inventory, storing products, processing large orders, picking and packing items, and coordinating shipments to customers.
Fulfillment centers leverage advanced technologies and streamlined processes to ensure quick turnaround times. These facilities are commonly used by e-commerce businesses, online retailers, and direct-to-consumer brands looking to enhance shipping efficiency and customer satisfaction. By outsourcing fulfillment, businesses can scale operations while minimizing logistical complexities and costs.
Key Functions of a Fulfillment Center
Here are the primary operations that make having your fulfillment center essential for retail success in today's world:
- Receiving Inventory: The primary goal of a fulfillment center is to accept incoming shipments from manufacturers or suppliers. They inspect goods for quality and accuracy, log received items into the inventory management system and assign storage locations for efficient retrieval.
- Storage: Products are systematically stored in designated locations within the fulfillment center, allowing for efficient inventory tracking and quick retrieval during order processing.
- Order Processing: When customers place retail or wholesale orders, the fulfillment center swiftly retrieves data, confirms stock availability, and prepares items for the next steps.
- Picking and Packing: Warehouse staff or automated systems pick ordered items, inspect them for accuracy, and securely pack them using appropriate materials to prevent damage during transit.
- Shipping: Once packed, orders are labeled, sorted, and handed over to shipping carriers for last-mile delivery, ensuring prompt and reliable shipment to customers.
Types of Fulfillment Centers
As the ecommerce business landscape evolves, various types of fulfillment centers have emerged to cater to different business needs:
- In-House Fulfillment Centers: Businesses that manage their own warehousing, inventory, and order processing operate in-house fulfillment centers. This model offers complete control over logistics but requires significant investment in infrastructure, technology, and personnel. It is ideal for companies with consistent order volumes and specialized fulfillment needs.
- Third-Party Logistics (3PL) Fulfillment Centers: 3PL fulfillment centers provide outsourced logistics services, handling inventory storage, order processing, packing, and shipping on behalf of businesses. These centers leverage advanced logistics networks to optimize costs and delivery speed. They are well-suited for a growing ecommerce store looking for scalable fulfillment solutions without maintaining their own warehouse facilities.
- Dropshipping Fulfillment Centers: These centers act as intermediaries between retailers and suppliers. When a customer places an order, the dedicated fulfillment center forwards it to the supplier, who ships the product directly to the customer. This model reduces inventory holding costs and is ideal for businesses seeking low-risk, flexible ecommerce fulfillment services.
- Hybrid Fulfillment Centers: These centres combine elements of different fulfillment models. Companies might use in-house fulfillment for core products and 3PL services for seasonal items or international orders. This approach offers flexibility and can be tailored to specific business needs.
Fulfillment Center vs. Traditional Warehouse
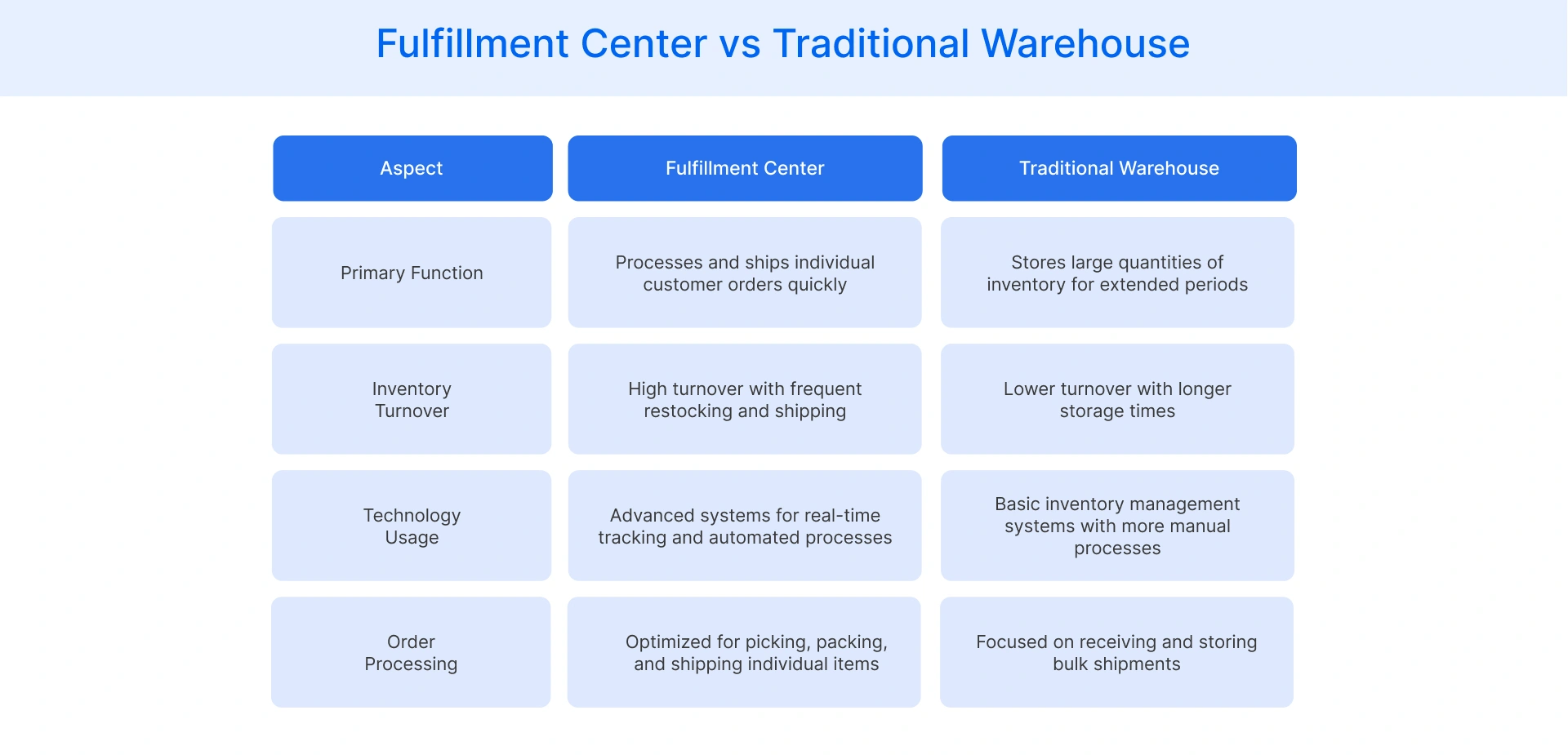
A fulfillment warehouse and a traditional warehouse serve different roles in the supply chain, with distinct functions, operations, and technology usage. While both store inventory, their core purpose differs significantly.
A typical warehouse primarily offers storage space for extended periods without immediate order processing. It is designed for bulk storage and wholesale distribution, often requiring manual inventory tracking and fewer technological integrations.
In contrast, fulfillment centers focus on fast order processing, packaging, and shipping, ensuring timely deliveries to customers. They operate with advanced technology, such as warehouse management systems (WMS) and automation, to optimize real-time order fulfillment. These centers offer a wide range of services to handle high inventory turnover and prioritize last-mile delivery.
How to Choose the Right Fulfillment Center?
Here are the steps you must follow to select a professional fulfillment center for your company:
Assess Business Needs
Evaluate your current order volume and product types to determine specific fulfillment requirements. Consider your growth projections and seasonal fluctuations to ensure the center can accommodate future needs. Analyze your customer demographics and shipping destinations to align with the fulfillment center’s capabilities.
Consider Strategic Locations
Choose fulfillment centers strategically located near your customer base to reduce shipping times and costs. Consider proximity to major transportation hubs and shipping carriers for efficient order processing. Evaluate multiple locations to create a network that optimizes delivery speed and minimizes transportation expenses.
Evaluate Technology Capabilities
Assess the fulfillment center’s technological infrastructure, including their warehouse management system and inventory tracking tools. Ensure their order processing software solutions can handle your business’s unique requirements and order complexities. Look for centers offering real-time visibility into inventory levels and order statuses to enhance your operational control.
Verify Scalability Options
Confirm that the fulfillment center can accommodate your business growth without disrupting business operations. Ensure they offer flexible storage options to handle inventory fluctuations during peak seasons or promotional periods. Verify their ability to scale order processing capacity to meet sudden increases in demand without compromising service quality.
Check Integration Capabilities
Ensure the fulfillment center’s systems can seamlessly integrate with your e-commerce platforms and marketplaces. Verify compatibility with your inventory management software to maintain accurate stock levels across all sales channels. Confirm that the center supports your preferred shipping carriers and can handle any special packaging or handling requirements.
Benefits of Using a Fulfillment Center
Here are the key benefits of using fulfillment centers by ecommerce companies:
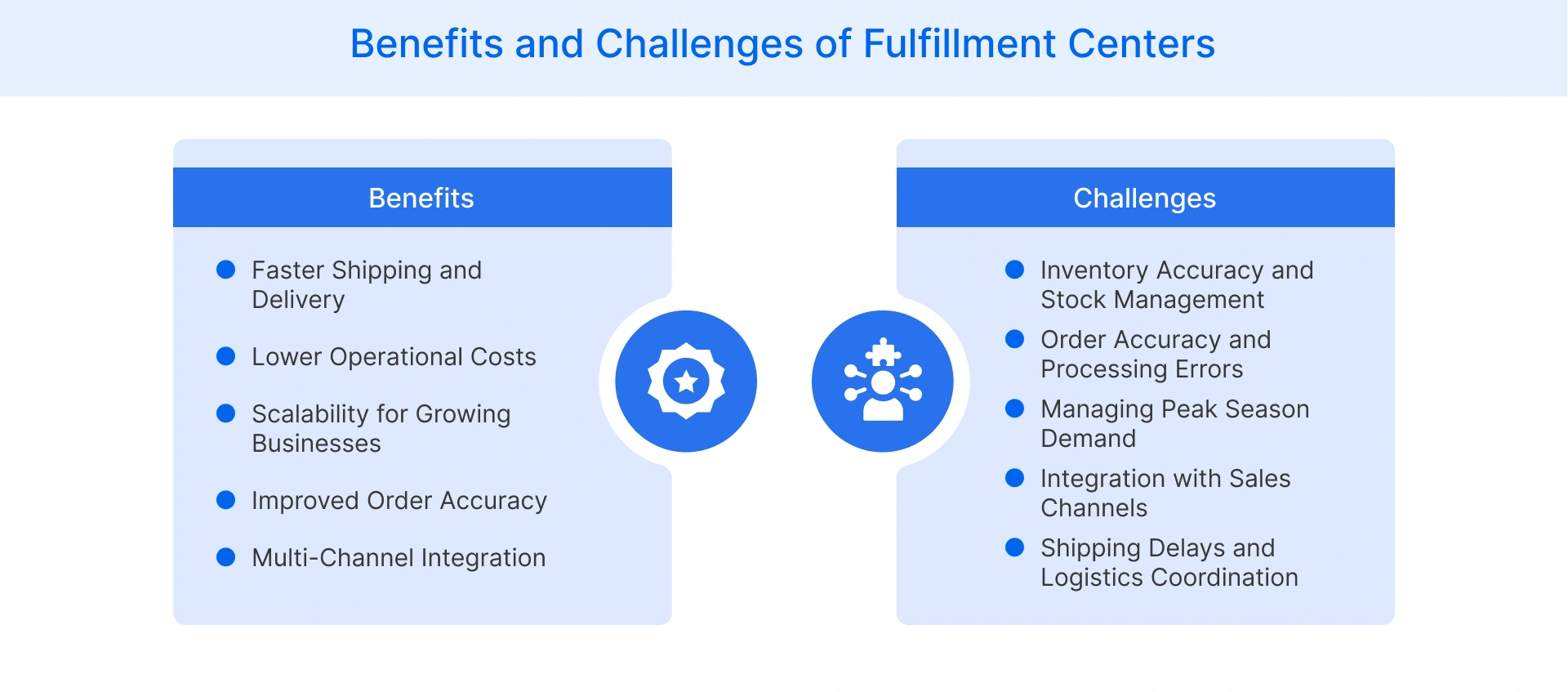
- Faster Shipping and Delivery: Fulfillment centers store a seller’s inventory near key markets, reducing transit times and ensuring a quick order fulfillment process. This improves delivery speed, enhances customer experience, and increases the likelihood of repeat purchases.
- Lower Operational Costs: Outsourcing fulfillment eliminates the need for warehouse space, staffing, and in-house logistics. Businesses can reduce overhead expenses while leveraging fulfillment centers’ bulk shipping discounts for cost-effective distribution.
- Scalability for Growing Businesses: A fulfillment center allows businesses to scale efficiently by adjusting storage and fulfillment capacity based on demand. This ensures seamless order processing during peak seasons without investing in additional infrastructure.
- Improved Order Accuracy: Advanced Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and automation tools enhance order picking, packing, and inventory tracking, reducing human errors and minimizing returns caused by incorrect shipments.
- Multi-Channel Integration: Fulfillment companies integrate e-commerce platforms, marketplaces, and shipping carriers, ensuring synchronized inventory management and seamless order processing across multiple sales channels.
Challenges in Fulfillment Center Operations
Managing a fulfillment center involves the following challenges:
- Inventory Accuracy and Stock Management: Poor inventory tracking can lead to overselling or stockouts, disrupting order fulfillment. Implementing real-time inventory management systems helps businesses maintain accurate stock levels and prevent fulfillment delays.
- Order Accuracy and Processing Errors: Picking and packing errors can result in incorrect shipments and customer dissatisfaction. Fulfillment centers rely on automation and barcode scanning to ensure accuracy and minimize returns.
- Managing Peak Season Demand: Sudden spikes in order volume during holidays or sales events can overwhelm fulfillment centers. Scalable storage and staffing solutions help manage increased demand efficiently without affecting processing times.
- Integration with Sales Channels: Syncing inventory and orders across multiple platforms requires robust integration. To avoid discrepancies, fulfillment centers must ensure seamless connectivity between e-commerce websites, marketplaces, and logistics providers.
- Shipping Delays and Logistics Coordination: Reliance on third-party carriers can lead to delays beyond the fulfillment center’s control. Strong partnerships with reliable shipping providers and advanced tracking systems help mitigate delays and improve delivery reliability.
Conclusion
A fulfillment center is a critical component of modern retail and e-commerce operations, ensuring seamless inventory management, efficient order processing, and fast delivery. By leveraging advanced technologies and analytics, fulfillment centers enhance operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
With innovations like FCC WMS and Pricing Intelligence solutions, businesses can streamline fulfillment, enhance demand forecasting, and maintain a competitive edge in the evolving digital ecosystem.
FAQ
A fulfillment provider manages returns by inspecting products, restocking inventory, or processing replacements. Reverse logistics systems ensure efficient handling of returned items, minimizing disruptions and maintaining customer satisfaction through streamlined refund or exchange processes.
Yes, a fulfillment center helps small businesses by reducing warehousing costs, managing inventory efficiently, and ensuring faster deliveries. It allows businesses to scale operations without investing in logistics infrastructure, improving customer experience and operational efficiency.
A fulfillment center focuses on processing individual customer orders, managing inventory, picking, packing, and shipping. A distribution center, however, primarily serves as a hub for bulk storage and large-scale product distribution to retailers or wholesalers.

