Table of Contents
- What is High-Low Pricing?
- How Does High-Low Pricing Strategy Work?
- Why is Reference Price Important in High-Low Pricing?
- When Should Retailers Use High-Low Pricing?
- How Can Retailers Set Up a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
- Examples of High-Low Pricing
- What are the Advantages of High-Low Pricing?
- What are the Disadvantages with High-Low Pricing?
- Conclusion
High-Low Pricing is a retail strategy where a product is launched at a premium price and later discounted through seasonal sales, clearance events, or limited promotions. This approach creates urgency, attracts diverse customer segments, and helps retailers optimise sales at different stages of a product’s lifecycle.
By maintaining initial high margins and offering discounts strategically, retailers influence buying behaviour without permanently lowering product value. High-Low Pricing is widely adopted in industries like fashion, electronics, and fast-moving consumer goods, where promotional events play a significant role in consumer decision-making.
Before proceeding, let’s understand the key features of high-low pricing:
- This strategy establishes a high initial price to create a strong value perception.
- It uses planned discounts and promotions to attract price-sensitive customer segments.
- The approach creates a sense of urgency, encouraging quicker purchase decisions from consumers.
- It helps you effectively manage and clear out aging or seasonal product inventory.
- This pricing model drives traffic to your store, both online and physical, during sales.
How Does High-Low Pricing Strategy Work?
The high-low pricing strategy operates on a cycle of alternating prices to maximize profitability and market reach. You begin by launching a product at a high initial price, often referred to as the reference price. This price targets early adopters and customers who are less price-sensitive and prioritize having the newest items. It establishes the product's perceived value and quality in the market.
After the initial launch period, you strategically introduce promotions, sales, or markdowns. This discounted price appeals to a broader, more price-conscious audience of bargain hunters. The significant difference between the original high price and the sale price creates a powerful psychological effect, making customers feel they are getting an excellent deal.
This generates a surge in sales volume and helps clear inventory. Once the promotional period ends, you can either return the product to its original high price or introduce a new cycle. This approach allows you to attract distinct customer groups at different times without permanently devaluing your products.
Why is Reference Price Important in High-Low Pricing?
The initial high price serves as a crucial psychological anchor, shaping customer perception of value for the product's entire lifecycle.
- Establishes Value Perception: The original price becomes the benchmark against which customers judge all future discounts, making the promotional price appear far more attractive and creating a stronger sense of a bargain.
- Creates a Sense of Urgency: A high reference price makes the limited-time discount feel like a significant opportunity that should not be missed, compelling customers to purchase quickly before the price increases again.
- Reinforces Brand Quality: A higher initial price can signal premium quality and desirability. When discounted, the product retains this perceived quality, unlike products that are always priced low.
- Maximizes Profit Margins: This strategy allows you to capture revenue from customers willing to pay the full price at launch, maximizing margins before appealing to bargain shoppers with planned markdowns.
- Increases Promotional Impact: The greater the difference between the reference price and the sale price, the more impactful the promotion feels, leading to higher sales volume and customer traffic during events.
When Should Retailers Use High-Low Pricing?
Retailers should consider using a high-low pricing strategy in specific scenarios where it can generate excitement and drive sales effectively. It is particularly powerful for seasonal items, such as holiday decorations or winter apparel, where demand peaks for a short period.
Sellers can introduce products at a high price at the beginning of the season and then discount them to clear stock as the season ends. This strategy is also highly effective for new product launches, especially in competitive markets like electronics and fashion. Starting with a premium price helps position the product and recover development costs from early adopters.
As the initial hype subsides, you can implement promotions to attract a wider audience. This allows you to capture maximum revenue from different customer segments over the product's lifecycle. High-low pricing is also an excellent tool for inventory management.
If you have overstocked items or products nearing the end of their lifecycle, a well-timed promotional event can quickly move this inventory. Retail sectors that see frequent product updates, such as fast-moving consumer goods and home goods, benefit greatly from this approach to maintain fresh and relevant stock.
How Can Retailers Set Up a High-Low Pricing Strategy?
Implementing a successful high-low pricing strategy requires a data-driven approach rather than guesswork to ensure profitability and brand integrity.
1. Identify Target Products and Categories
Analyze historical sales data, market trends, and product lifecycle stages to select items best suited for high-low pricing. Focus on products with high perceived value, seasonal demand, or those in competitive categories where promotions can effectively capture market share. Utilize analytics to determine which items are likely to generate the most traffic.
2. Establish the Initial High Price
Determine a credible initial price by evaluating competitor pricing, production costs, and the product's unique value proposition. This reference price must be high enough to establish a premium perception and secure healthy margins from early buyers, but realistic enough to avoid alienating your entire customer base from the start.
3. Plan Promotional Discounts Strategically
Develop a promotional calendar that aligns with seasonal peaks, holidays, and internal business goals, such as inventory clearance. Use forecasting models to determine the optimal discount depth and duration. Avoid constant sales, which can train customers to wait for discounts and erode your brand's value over time.
4. Implement a High-Low Pricing Solution
Utilize an advanced tool like Flipkart Commerce Cloud’s Pricing Manager to automate and optimize your strategy. This solution uses AI-driven competitive intelligence and a dynamic rules engine to adjust prices in real time based on market conditions, ensuring your promotions are both competitive and profitable across thousands of SKUs.
5. Monitor Sales Performance and Adjust
Continuously track key metrics such as sales volume, profit margins, and customer traffic during and after promotions. Leverage the insights from your pricing solution to understand customer responses, refine your discounting schedules, and make agile adjustments to your strategy, ensuring sustained profitability and market relevance.
Examples of High-Low Pricing
Here are three real-world examples of major brands that have successfully implemented the high-low pricing strategy in their operations.
- Macy’s: The department store is well-known for its frequent sales events, such as its "One Day Sale." It introduces new clothing and home goods at a full price and then uses planned promotions and clearance racks to attract bargain-hunters.
- Best Buy: This electronics retailer launches new gadgets like TVs and laptops at a premium price for early adopters. It later implements significant seasonal discounts during periods like Black Friday to move inventory and capture a broader market share.
- Nike: In the fashion and athletic apparel industry, Nike often releases new sneaker designs at a high price point. After the initial demand from enthusiasts wanes, these products are usually included in seasonal sales to appeal to more price-sensitive consumers.
What are the Advantages of High-Low Pricing?
This pricing strategy offers several distinct benefits that can help you increase revenue, manage inventory, and attract a diverse customer base.
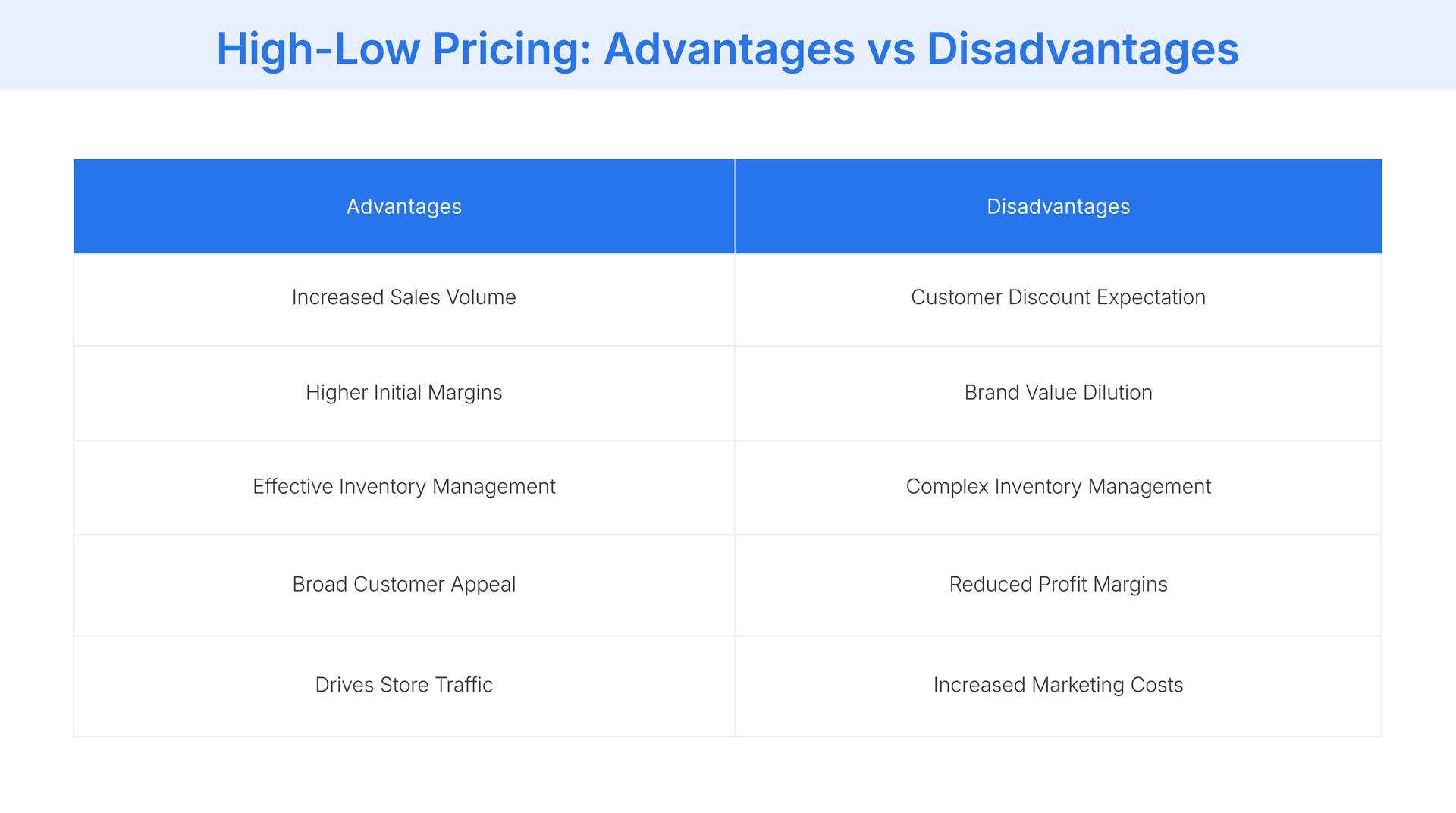
- Increased Sales Volume: Promotions and discounts create excitement and urgency, resulting in significant sales spikes and attracting a higher volume of customers to your store during promotional periods.
- Higher Initial Margins: By launching products at a premium price point, you can secure higher profit margins from early adopters and customers who are not focused on finding discounts.
- Effective Inventory Management: High-low pricing is an excellent tool for clearing out seasonal or old inventory efficiently, preventing overstock situations and making room for new products on your shelves.
- Broad Customer Appeal: The strategy allows you to cater to two different market segments: premium shoppers who want the latest products and bargain hunters who wait for a good deal.
- Drives Store Traffic: Well-marketed sales events can significantly boost both online and in-store traffic, creating opportunities for customers to purchase other full-priced items during their visit.
What are the Disadvantages with High-Low Pricing?
While effective, this strategy also comes with potential drawbacks that must be managed carefully to protect your brand and profitability.
- Customer Discount Expectation: If promotions are too frequent, customers may learn to wait for sales and refuse to buy products at their full price, potentially harming your initial margins.
- Brand Value Dilution: Offering constant and deep discounts can negatively impact your brand's image over time, making it appear less premium and eroding the perceived value of your products.
- Complex Inventory Management: The strategy's success relies on accurately forecasting demand for both full-price and sale periods, which can be complex and lead to stockouts or overstock if managed poorly.
- Reduced Profit Margins: While sales increase volume, they also lower the profit margin on each item sold. Poor planning can lead to lower overall profitability despite higher revenue during promotions.
- Increased Marketing Costs: Each promotional event requires a dedicated marketing effort to inform customers and drive traffic, which can add significant costs to your operational budget over time.
Conclusion
High-low pricing remains a powerful and widely used strategy in the competitive retail landscape. When executed thoughtfully, it allows you to balance the need for profitability with the demand for customer engagement. By leveraging robust pricing tools and data-driven insights, you can create compelling offers that drive sales without sacrificing your brand’s long-term value.
FAQ
High-low pricing involves starting with a high price and offering frequent promotions, creating excitement. In contrast, EDLP, used by retailers like Walmart, focuses on maintaining consistently low prices over a long period, offering reliability and predictability to customers instead of promotional rushes.
Retailers in industries with seasonal demand or frequent product turnover, such as fashion, electronics, and home goods, benefit the most. This strategy is ideal for businesses that want to create excitement around new launches and effectively clear out old inventory through planned sales events.
Price skimming involves setting a very high initial price for an innovative new product and gradually lowering it over a long period as the market evolves. High-low pricing is more cyclical, with frequent, temporary promotions on existing products rather than a permanent, slow price reduction.
Yes, it can have mixed effects. While promotions can attract new customers, over-reliance on discounts may train loyal customers to wait for sales, potentially eroding their willingness to pay full price. A balanced approach is key to maintaining both engagement and loyalty.
Seasonal trends are a primary driver for high-low pricing. Retailers often launch seasonal collections at full price to capture peak demand and then use markdowns as the season wanes to clear inventory. This aligns pricing directly with fluctuating consumer interest throughout the year.
Retailers can use advanced pricing solutions like Flipkart Commerce Cloud’s Pricing Manager. Our platform utilizes AI and machine learning to monitor competitor prices, analyze market demand, and automate price adjustments, ensuring that your high-low strategy remains both competitive and profitable.

