Table of Contents
- What is Mobile Commerce?
- What are the Key Features of Mobile Commerce?
- How is Mobile Commerce Different from E-commerce?
- What Are the Key Benefits of Mobile Commerce for Retailers?
- How Do Businesses Create a Successful Mobile Commerce Strategy?
- What Technologies Power Mobile Commerce?
- Conclusion
Mobile commerce, popularly known as m-commerce, is a branch of electronic commerce that involves the selling of goods and services directly through mobile phones and handheld devices such as smartphones and tablets. Unlike traditional ecommerce, which may rely on desktops or laptops, m-commerce enables mobile transactions from virtually anywhere, offering greater convenience and accessibility.
The concept has seen rapid growth with the rise of internet access, improved mobile technology, and secure payment methods. Mobile commerce covers online shopping, mobile banking, mobile ticketing, financial services, and even in-app transactions across entertainment and subscription platforms.
Key aspects of mobile commerce include:
- Mobile commerce enables transactions on wireless handheld devices, eliminating the need for desktop dependency.
- It provides flexible mobile shopping experiences with quick access to products and services.
- Secure mobile payment apps enable fast and trustworthy transactions.
- Retailers use mobile commerce apps to personalize and optimize the customer journey.
- It supports both online retail and service-oriented purchases in one ecosystem.
What are the Key Features of M-Commerce?
The architecture of mobile commerce is built on several distinct features that cater specifically to the on-the-go consumer.
- Ubiquity: Mobile platforms enable transactions anytime, anywhere, expanding retail sales across geographies, including the United States and beyond.
- Convenience: Shopping is simplified through intuitive interfaces, streamlined checkout processes, and mobile payment options, allowing customers to complete purchases with just a few taps on their screens.
- Personalization: Retailers can use device data, such as location and browsing history, to deliver highly targeted offers, product recommendations, and marketing messages directly to individual users.
- Accessibility: M-commerce platforms are always available on a device that users carry with them constantly, making it easy for businesses to engage with customers throughout their day.
- Integrated Technologies: It leverages built-in device features like cameras for QR code scanning, GPS for location-based services, and biometrics for secure, one-touch payments, creating a richer experience.
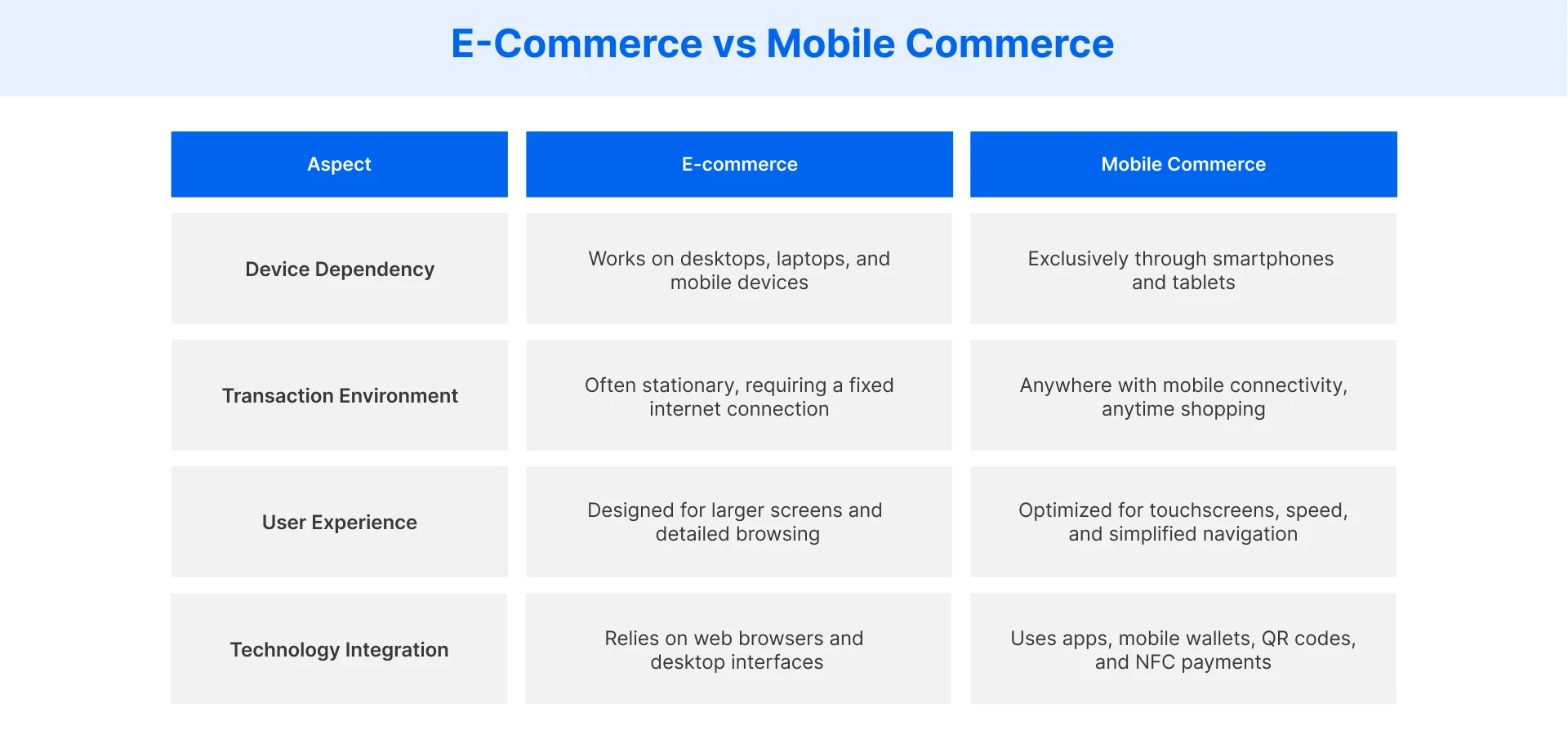
How is Mobile Commerce Different from E-commerce?
E-commerce spans desktops, laptops, and mobile, while mobile commerce is device-specific, optimized for mobile shoppers. Its strength lies in mobile platforms that enhance online shopping experiences, ensure higher conversion rates, and use mobile commerce apps for seamless navigation.
What Are the Key Benefits of Mobile Commerce for Retailers?
Adopting a mobile commerce strategy offers retailers significant advantages in reaching and retaining a customer base in a competitive marketplace.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: Retailers can provide a seamless and convenient shopping journey with mobile-optimized designs, personalized content, and simplified checkout processes, which increases overall customer satisfaction.
- Increased Customer Reach: With the global proliferation of smartphones, businesses can connect with a much broader and more diverse audience that may not use traditional desktop computers for shopping.
- Higher Engagement Rates: Features like push notifications and in-app messaging allow for direct and immediate communication, helping retailers to nurture customer relationships and drive repeat purchases more effectively.
- Deeper Customer Insights: Mobile devices provide access to rich customer data, including location, behavior, and preferences, enabling retailers to refine their marketing strategies and product offerings for better results.
- Omnichannel Integration: M-commerce acts as a crucial bridge between online and offline retail channels, supporting functionalities like click-and-collect, in-store navigation, and mobile payments at physical locations.
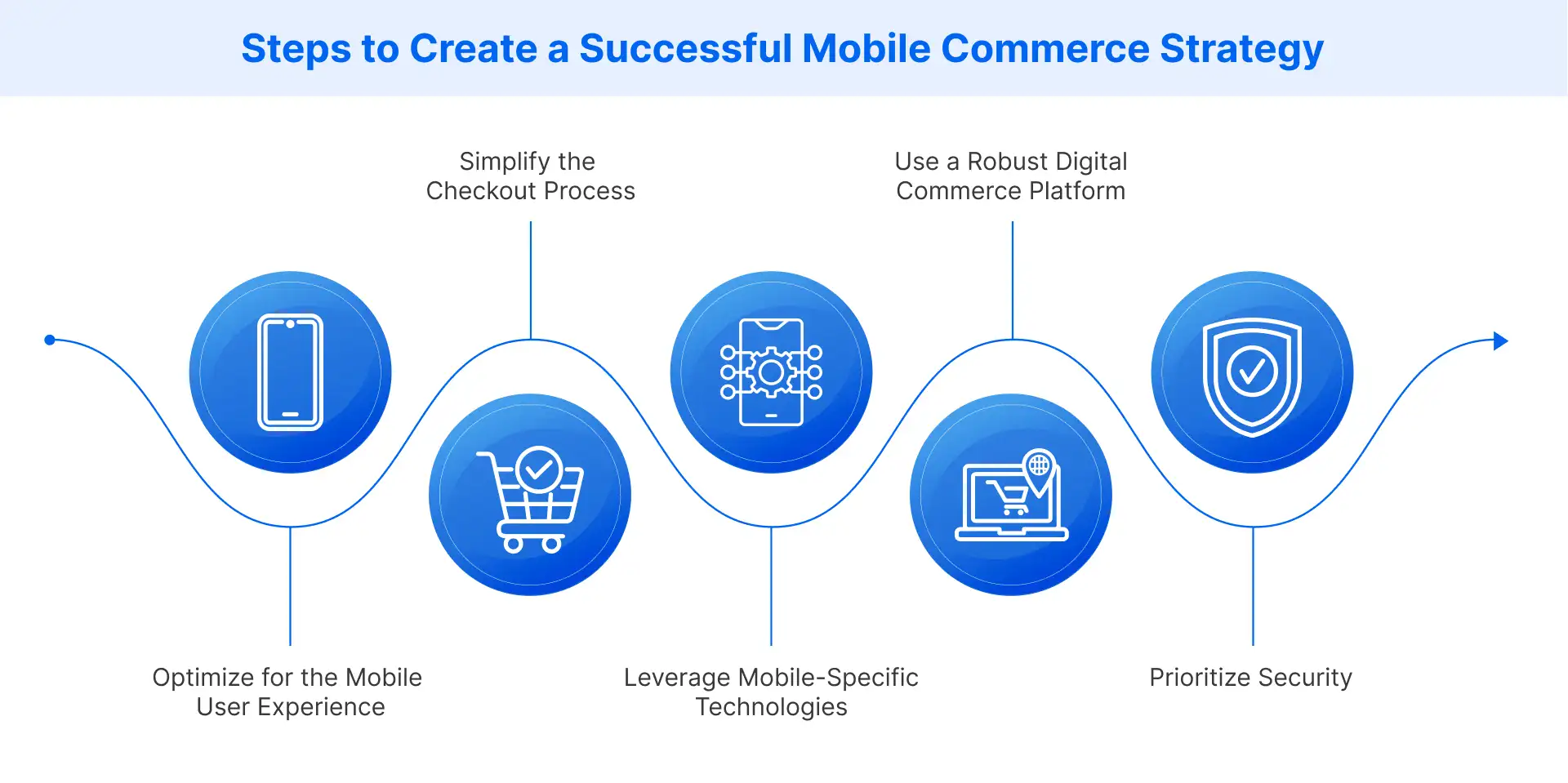
How Do Businesses Create a Successful Mobile Commerce Strategy?
Building an effective mobile commerce strategy requires a technical approach focused on performance, user experience, and security.
Optimize for the Mobile User Experience
A successful mobile presence begins with a design philosophy prioritizing the mobile user. This involves implementing responsive or adaptive web design to ensure the interface renders perfectly on all screen sizes.
Key technical considerations include:
- Optimizing image and asset delivery through Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) to reduce load times
- Simplifying navigation with thumb-friendly touch targets
- Adhering to platform-specific guidelines like Apple's Human Interface Guidelines or Google's Material Design for native apps.
Simplify the Checkout Process
High cart abandonment rates on mobile are often due to cumbersome checkout flows. To mitigate this, integrate mobile-native payment solutions like Apple Pay and Google Pay, which use biometric authentication (Face ID, fingerprint scan) for one-tap transactions.
Implementing a guest checkout option reduces friction for new customers. For returning users, securely saving payment and shipping details through tokenization allows for a true one-click ordering experience, dramatically increasing conversion rates.
Leverage Mobile-Specific Technologies
Go beyond a simple mobile storefront by integrating features unique to mobile devices. Utilize push notifications for personalized, real-time engagement, such as abandoned cart reminders or location-based promotions triggered by geofencing.
Incorporate augmented reality (AR) for virtual try-on experiences or QR code scanners to bridge the gap between physical and digital channels. In-app messaging can also provide instant customer support without forcing users to leave the application.
Use a Robust Digital Commerce Platform
A scalable mobile commerce strategy depends on a powerful backend. A comprehensive platform is essential, and solutions like Flipkart Commerce Cloud (FCC) provide the foundational technology for building composable, scalable, and personalized mobile storefronts.
This API-first architecture allows for faster updates, easier integration with third-party services (like CRM or analytics), and the ability to deliver consistent experiences across both mobile apps and mobile websites from a single, centralized backend.
Prioritize Security
Consumer trust is paramount in mobile commerce. Implement multi-layered security protocols to protect sensitive data. This includes end-to-end encryption for all data in transit, adherence to PCI DSS standards for payment processing, and the use of tokenization to replace actual credit card numbers with unique identifiers.
Offering multi-factor authentication (MFA) provides an additional layer of security for user accounts, protecting both the customer and the business from fraudulent activities.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of M-Commerce?
By 2026, mobile commerce has become the main way we shop, making up nearly 60% of all online sales with a value of $2.8 trillion. This huge growth is happening because mobile wallets and social media make it easy to buy things in seconds, but it also means businesses must work harder to fix slow speeds and keep customer data safe.
While shopping on a phone is faster than ever, it comes with a few clear trade-offs. To help you decide if a mobile-first plan is right for you, here are the main pros and cons.
|
Category |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
User Experience |
Enables shopping anywhere, anytime. Features like mobile wallets and biometrics make transactions nearly frictionless. |
Smaller interfaces can make complex product comparisons difficult or lead to accidental clicks. |
|
Marketing |
Uses location tracking and user behavior data to send timely, relevant push notifications. |
Constant tracking and data collection can lead to significant security concerns and user distrust if not handled transparently. |
|
Operations |
Seamlessly connects online browsing with physical stores via QR codes and click-and-collect. |
Maintaining high-performance mobile applications across different operating systems requires significant investment. |
|
Connectivity |
Leverages social media platforms to turn discovery into immediate social commerce sales. |
Poor 5G or Wi-Fi signals in certain areas can disrupt the checkout process and lead to high cart abandonment. |
To effectively implement the advantages listed above, businesses must understand how different technologies interact to facilitate a single transaction.
What Technologies Power Mobile Commerce?
Several core technologies work together to create the seamless and responsive experience that defines modern mobile commerce.
- Native and Web Apps: Native apps are built for a specific OS (iOS/Android) for optimal performance. At the same time, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) offer app-like experiences directly through a mobile browser.
- Responsive Web Design: This approach uses flexible grids and CSS media queries, allowing a single website to automatically adapt its layout to fit the screen size of any device.
- Digital Wallets: Services like Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay securely store payment information on a device, enabling fast and secure transactions via NFC or QR codes.
- NFC (Near Field Communication): This technology allows two devices in proximity to exchange data, facilitating contactless payments where users can simply tap their phone at a compatible terminal.
- QR Codes (Quick Response): These two-dimensional barcodes are scanned by a phone’s camera to quickly link users to websites, product pages, or payment portals without manual data entry.
- 5G Connectivity: The latest generation of mobile networks provides faster speeds and lower latency, enabling richer mobile experiences like high-definition video streaming and augmented reality shopping features.
Conclusion
Mobile commerce has evolved from a niche channel into a cornerstone of modern retail strategy. Its growth is driven by consumer demand for convenience, personalization, and immediacy. For retailers, embracing m-commerce is a necessity to stay competitive, engage with customers effectively, and drive sustainable growth in an increasingly mobile-first world.
FAQ
M-commerce is most commonly used for retail shopping, bill payments, and booking services through mobile shopping apps. Consumers increasingly rely on mobile wallets for contactless in-store payments and social media for discovering new brands. This ubiquity makes a robust mobile commerce strategy essential for modern retailers to remain competitive.
The different types of mobile commerce include mobile shopping, online banking, and mobile wallets like Google Wallet. It also encompasses social commerce, where transactions happen directly on social media platforms. These diverse mobile applications allow customers to complete online transactions quickly and securely while they are on the go.
Businesses measure the success of their mobile commerce efforts by tracking conversion rates, average order value, and the total number of smartphone users engaging with their platform. Monitoring app store ratings and participation in loyalty programs provides deep insight. These metrics help retailers identify the next step for growth.
A mobile-optimized website is essential for broad reach and search visibility. A native app is better for fostering loyalty and engagement with repeat customers through features like push notifications and a more controlled user experience. Many businesses benefit from having both.
M-commerce can bridge the physical and digital gap. It enables click-and-collect services, allows customers to check in-store inventory from their phones, and facilitates contactless payments. Geolocation can also be used to send targeted offers to customers near a physical store.
Key risks include insecure Wi-Fi connections, malware or fraudulent apps that can steal personal data, and phishing attacks. Businesses must implement robust security measures like encryption, tokenization, and multi-factor authentication to protect customer information and build trust.
A mobile wallet (e.g., Apple Pay) is an application that securely stores your payment card information. A mobile payment is the actual transaction process of using a mobile device to pay for goods or services, often facilitated by a mobile wallet.
Personalization uses data collected from a user's device and behavior, such as browsing history, purchase patterns, and location, to tailor the shopping experience. This can include showing relevant product recommendations, sending targeted promotions, and customizing the app or website interface.

